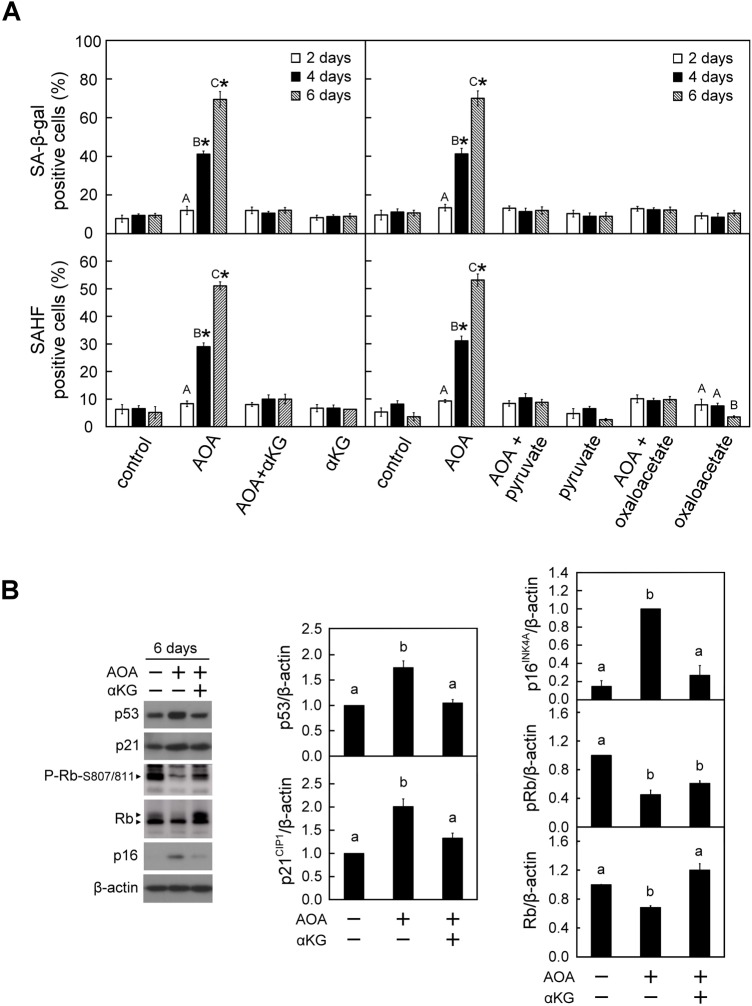
Fig. 3.
Prolonged blockade of glutamine-dependent anaplerosis with AOA triggered cellular senescence in WI38 cells. WI38 cells were treated with vehicle or AOA in the absence or presence of anaplerotic factors αKG, pyruvate or oxaloacetate for the indicated time-period as described in Fig. 1A. (A) Effect of AOA on cellular senescence. The senescent cells were assessed using the SA-β-gal and SAHF staining assays. Upper panel: SA-β-gal positive cells were counted in at least 10 microscopic fields in each of the triplicate cultures of all treatment groups. The percentage of SA-β-gal positive cells was calculated relative to the total cell number in the counted fields. Lower panel: A total of 200 cells from each of the indicated treatment samples were examined for SAHF formation. The percentage of SAHF-positive cells was calculated relative to the total cell number in the counted fields. (B) Effect of AOA on senescence-inducing regulators. After treatment for 6 days, cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting and densitometry analysis for p53, p21CIP1, Rb, P-Rb-S807/811 and p16INK4A, β-actin served as a loading control. The arrowheads show the indicated antibody recognized specific signals. All quantitative data are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. (n=3) of three independent experiments. Different uppercase letters indicate significant difference of the same treatment group at different time-points (P<0.05). Asterisk (*) designates a significant difference compared with the respective vehicle control at the same time-point (P<0.05). Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatment groups (P<0.05).