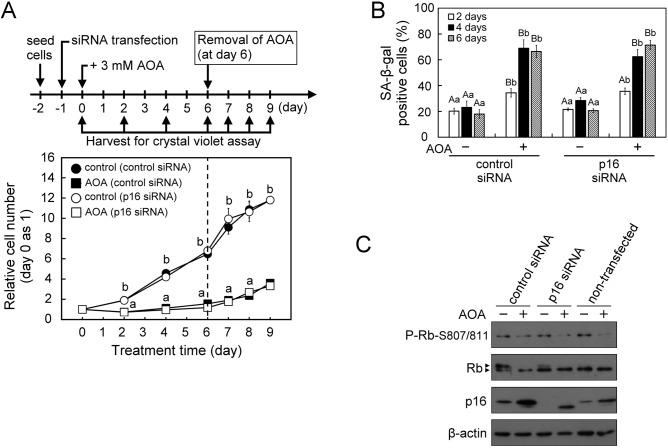
Fig. 5.
AOA treatment leads to inhibition of proliferation, increase of p16 antibody-reactive p12 and cellular senescence in p16INK4A-knockdown WI38 cells. Cells were first transfected with p16INK4A siRNA or control siRNA for 24 h, and then treated with vehicle or 3 mM AOA in fresh medium for the indicated time-periods with medium changed at 2-day intervals. (A) Effect of 6-day AOA treatment and 3-day AOA removal on cell proliferation. The relative cell numbers were calculated by normalizing against the value of day 0. After 6 days of AOA treatment, cells were refreshed with AOA-free growth medium and incubated for an additional 3 days. (B) Effect of AOA on cellular senescence. The senescent cells were assessed using the SA-β-gal staining assay. SA-β-gal positive cells were counted in at least five microscopic fields each of the triplicate cultures of all treatment groups. The percentage of SA-β-gal positive cells was calculated relative to the total cell number (DAPI-stained positive cells) in the counted fields. (C) Effect of AOA on the senescence-inducing regulator p16INK4A−Rb pathway. At the end of 6-day AOA treatment, cell lysates were prepared for immunoblotting and densitometry analysis of p16INK4A, Rb and P-Rb-S807/811 with β-actin served as a loading control. All quantitative data are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. (n=5) of two independent experiments. The arrowheads show the indicated antibody recognized specific signals. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatment groups at the same time-point (P<0.05). Different uppercase letters indicate significant difference of the same treatment group at different time-points (P<0.05).