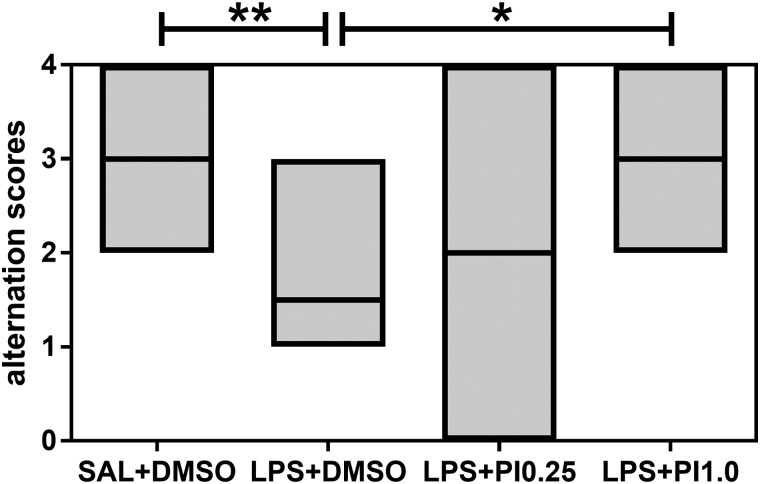
Fig. 1.
T-maze. The effects of prenatal LPS (100 µg/kg at GD 9.5) and postnatal pioglitazone [0.25 and 1.0 mg/kg/day between postnatal days (PND) 21 and 29] exposures on the T-maze spontaneous alternation test in juvenile male rat offspring. SAL+DMSO, prenatal saline injection and postnatal daily DMSO injection; LPS+DMSO, prenatal LPS injection and postnatal daily DMSO injection; LPS+PI0.25, prenatal LPS injection and postnatal pioglitazone 0.25 mg/kg/day; LPS+PI1.0, prenatal LPS injection and postnatal pioglitazone 1.0 mg/kg/day (n=8 rats/group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's test). The data are expressed as the median (minimum and maximum).