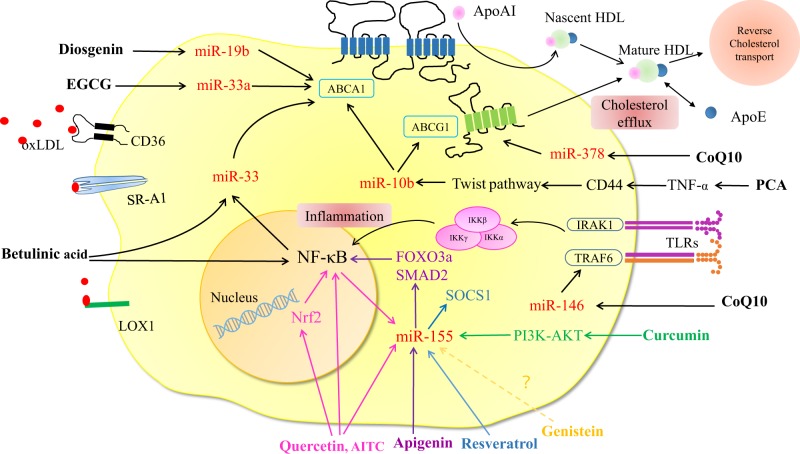
Fig. 2.
Dietary compounds regulate AS-related macrophage cholesterol metabolism and inflammation via miRNAs. Different food compounds play atheroprotective roles by various miRNAs via different signaling pathways. (1) Diosgenin, EGCG, betulinic acid, CoQ10, and PCA could increase cholesterol efflux by inhibiting miR-19b, miR-33, miR-378, miR-33, and miR-10b, respectively. (2) Quercetin, AITC, apigenin, curcumin, and resveratrol could inhibit inflammatory response, through targeting to miR-155. CoQ10 could regulate inflammation via inhibiting miR-146a. With regard to the macrophage inflammation, different color lines represent the different dietary compounds regulate diverse signaling pathways via different miRNAs. AITC, allyl-isothiocyanate; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; PCA protocatechuic acid