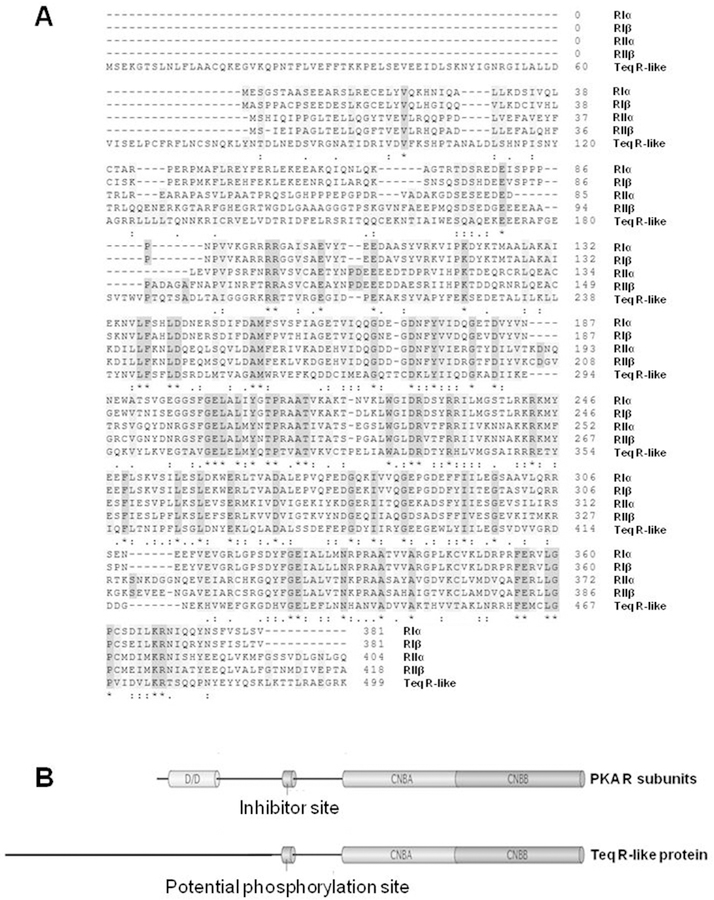
Fig. 2. Comparison of the primary structure and domain organization of the T. equiperdum R-like protein and the four human PKA R subunit isoforms.
A, Alignment of amino acid sequences of the R-like protein from T. equiperdum and the RIα, RIβ, RIIα, and RIIβ subunits from human [Accesion No. P10644.1, P31321.4, P13861.2 and P31323.3, respectively using the NCBI Protein database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/)]. Identical residues are shown with an asterisk (*), conservative substitutions are labeled with a colon punctuation mark (:), and semi-conservative substitutions are labeled with a period (.). B, The standard domain structure of mammalian PKA R subunits is contrasted to the domain organization of the Teq R-like protein. CNBA and CNBB = cyclic nucleotide binding domains A and B, respectively; D/D = dimerization and docking domain.