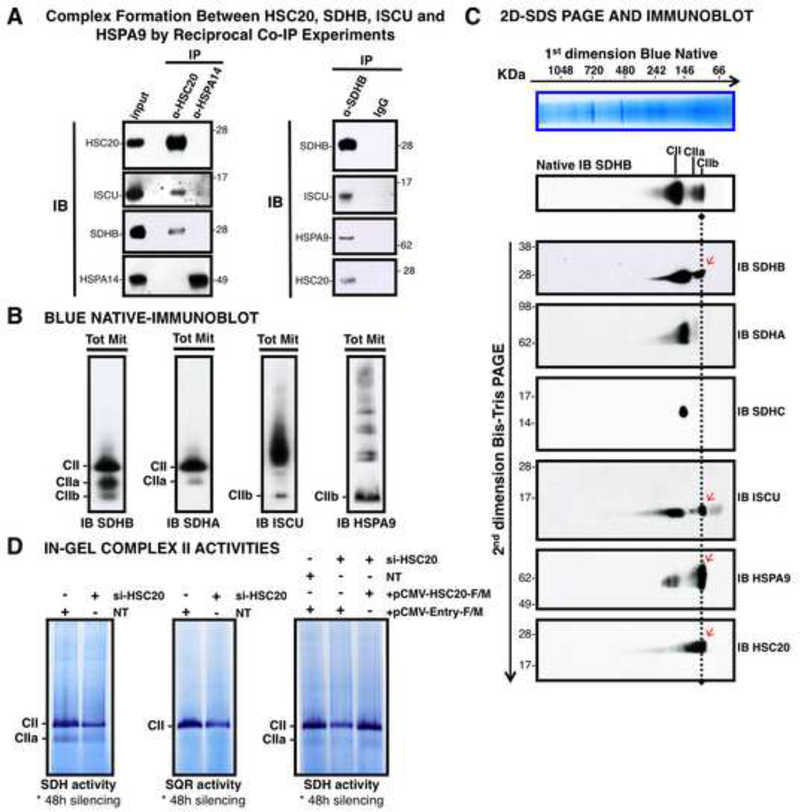
Figure 2. HSC20 Binds SDHB and Forms a Complex with HSPA9 and ISCU.
(A) Complex formation between HSC20, SDHB, ISCU and HSPA9 by reciprocal co-IP experiments. IP of HSC20 or HSPA14, followed by IBs to ISCU, SDHB, HSPA14. HSPA14 did not interact with HSC20 (IB to HSC20), and represented a false positive from the Y2H screen (left panel). IP of SDHB, followed by IBs to ISCU, HSPA9, HSC20 revealed that there was a complex composed of SDHB, ISCU, HSPA9 and HSC20 (right panel), (n= 5 biological samples). (B, C) BN and 2D-BN-SDS IBs of mitochondrial extracts resolved three SDHB-containing complexes of distinctive composition. Red arrows indicate components of the CIIb complex. (D) Response of in-gel SDH and SQR activities of Complex II to silencing of HSC20, and rescue by HSC20-F/M. NT represents a control extract from cells transfected with non-targeting si-RNAs. (B-D, n = 4 biological samples). See also Figure S2.