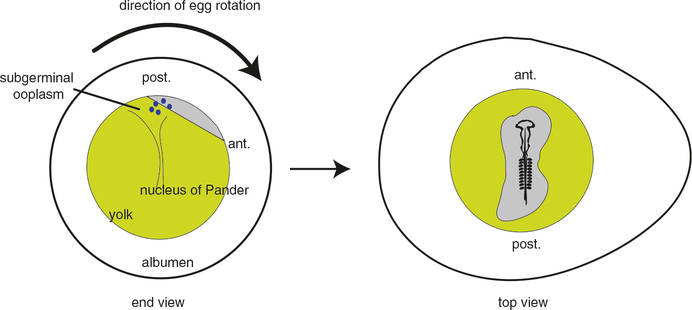
Fig. 5.
Model for establishment of asymmetry in bird eggs. Left, sectional view of a uterine chicken egg viewed from the sharp end. The direction of rotation is indicated; because of this rotation, the lighter blastoderm cytoplasm is maintained off angle as it continually floats to the highest point. The blastoderm is exposed to the subgerminal cytoplasm, which is hypothesized to contain axis determinants (blue). At this stage, the blastoderm is several thousand cells and has not formed the area pellucida epiblast. Right, top view of 2–3 day embryo showing anterior-to-posterior axial polarity. This embryo would conform to von Baer’s rule, with head oriented away with the blunt end positioned left. ant. anterior, post. posterior