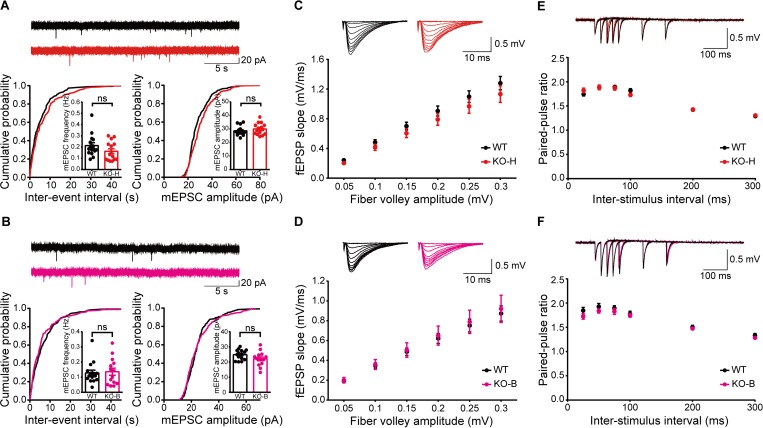
Fig 2. Ngl3−/−(Hyb) and Ngl3−/−(B6) mice show normal excitatory spontaneous and basal synaptic transmission.
(A) Normal AMPAR mEPSCs in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons of Ngl3−/−(Hyb) mice (P21–23). n = 15 cells from three mice for WT and KO; ns, not significant, Student t test. (B) Normal AMPAR mEPSCs in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons of Ngl3−/−(B6) mice (P22–25). n = 15 cells from three mice for WT and 14, 4 for KO; ns, not significant, Student t test. (C and E) Normal input-output relationship and paired-pulse ratio at hippocampal SC-CA1 synapses of Ngl3−/−(Hyb) mice (P28–30), as shown by fEPSP slopes plotted against either fiber volley amplitudes or inter-pulse intervals. n = 10 slices from three mice for WT and KO for both input-output and paired-pulse ratio, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test. (D and F) Normal input-output relationship and paired-pulse ratio at hippocampal SC-CA1 synapses of Ngl3−/−(B6) mice (P28–30), as shown by fEPSP slopes plotted against either fiber volley amplitudes or inter-pulse intervals. n = 7 slices from two mice for WT and KO for both input-output and paired-pulse ratio, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test. Primary data can be found in S3 Data. AMPAR, AMPA receptor; CA1, Cornu Ammonis 1; fEPSP, field excitatory postsynaptic potential; KO, knockout; KO-B, knockout, C57BL/6; KO-H, knockout, hybrid; mEPSC, miniature excitatory postsynaptic current; ns, not significant; P, postnatal day; SC-CA1, Schaffer collateral-CA1 pyramidal; WT, wild-type.