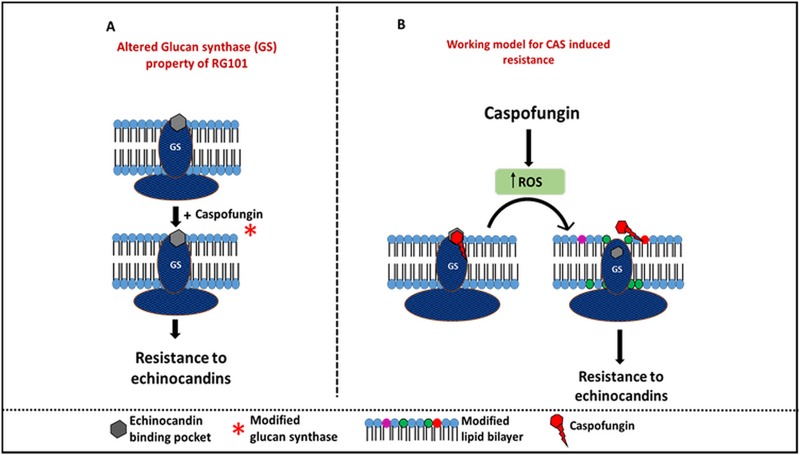
FIG 7.
Working model showing the non-fks1 mutation-mediated mechanism of resistance in RG101. (A) Addition of CAS during growth of RG101 altered the properties of glucan synthase, rendering it resistant to CAS, at both the cellular and enzyme levels. (B) Working model for CAS-induced resistance in RG101. CAS induces ROS production in cells. We hypothesize that high ROS levels alter the lipid composition in the microenvironment of glucan synthase, causing a conformational change in glucan synthase and leading to CAS resistance.