Figure 2.
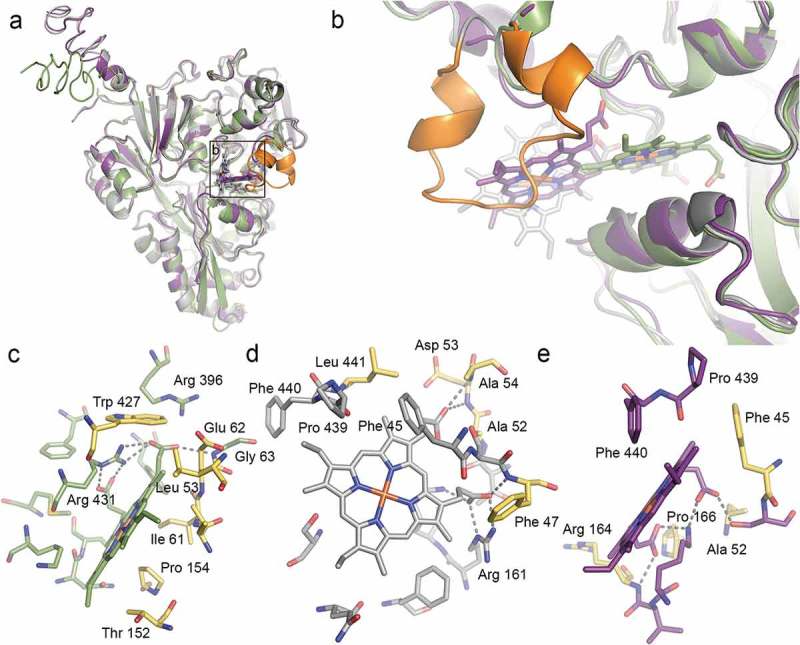
Structural prediction of heme binding to HbpA and SapA. HADDOCK was used to dock heme B to homology models of HbpA (green), full-length SapA (grey) and truncated SapA (purple) in which a non-conserved loop consisting of residues 140–158 has been removed. The truncated residues are colored orange in full-length SapA. (a) Overlay of the best scoring docking solutions for HbpA, SapA and truncated SapA. (b) Zoom-in on predicted heme binding sites showing how HbpA binds heme deeper into the ligand-binding pocket. In full-length SapA, the non-conserved loop (orange) prevents heme binding into the same pocket whereas in truncated SapA, the pocket is more accessible. (c-e) LigPlot+ analysis of the predicted heme binding site in HbpA (c), full-length SapA (d) and truncated SapA (e) with residues lining the binding sites in stick representation. Predicted hydrogen bonds are showed as dashed lines. Residues that are common for all three binding sites are colored yellow.
