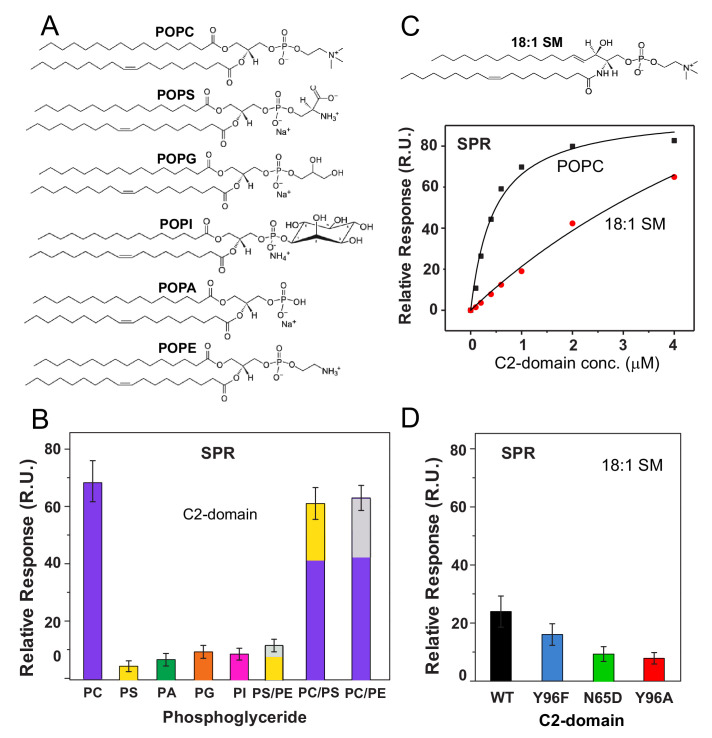
Figure 4. cPLA2α C2-domain binding affinity for phosphoglyceride and sphingomyelin (SM) vesicles.
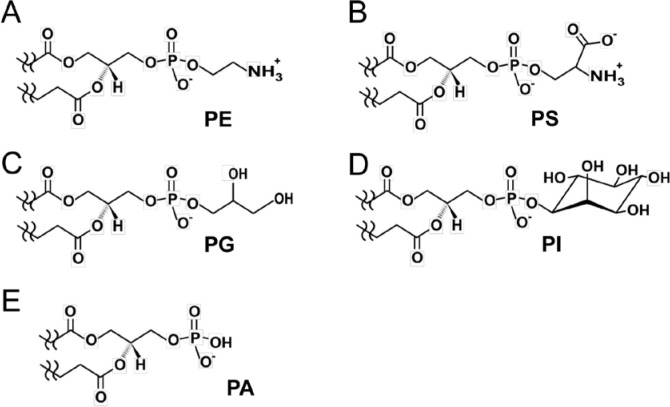
(A) Phosphoglyceride structural formulas. (B) Relative affinities of the C2-domain (1 μM) for different phosphoglycerides obtained by SPR. Molar ratios for PS/PE, PC/PS and PC/PE mixed composition vesicles are 7:3. (see Figure 4—figure supplement 1). (C) SPR binding isotherms showing C2-domain equilibrium adsorption to immobilized POPC or 18:1-SM vesicles as a function of protein concentration (see Figure 4—figure supplement 2 for additional information). (D) Effect of C2-domain mutations (1 μM) on binding to 18:1 SM obtained by SPR (see 'Materials and methods' for other details).
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Assessment of C2-domain binding to different phosphoglycerides.
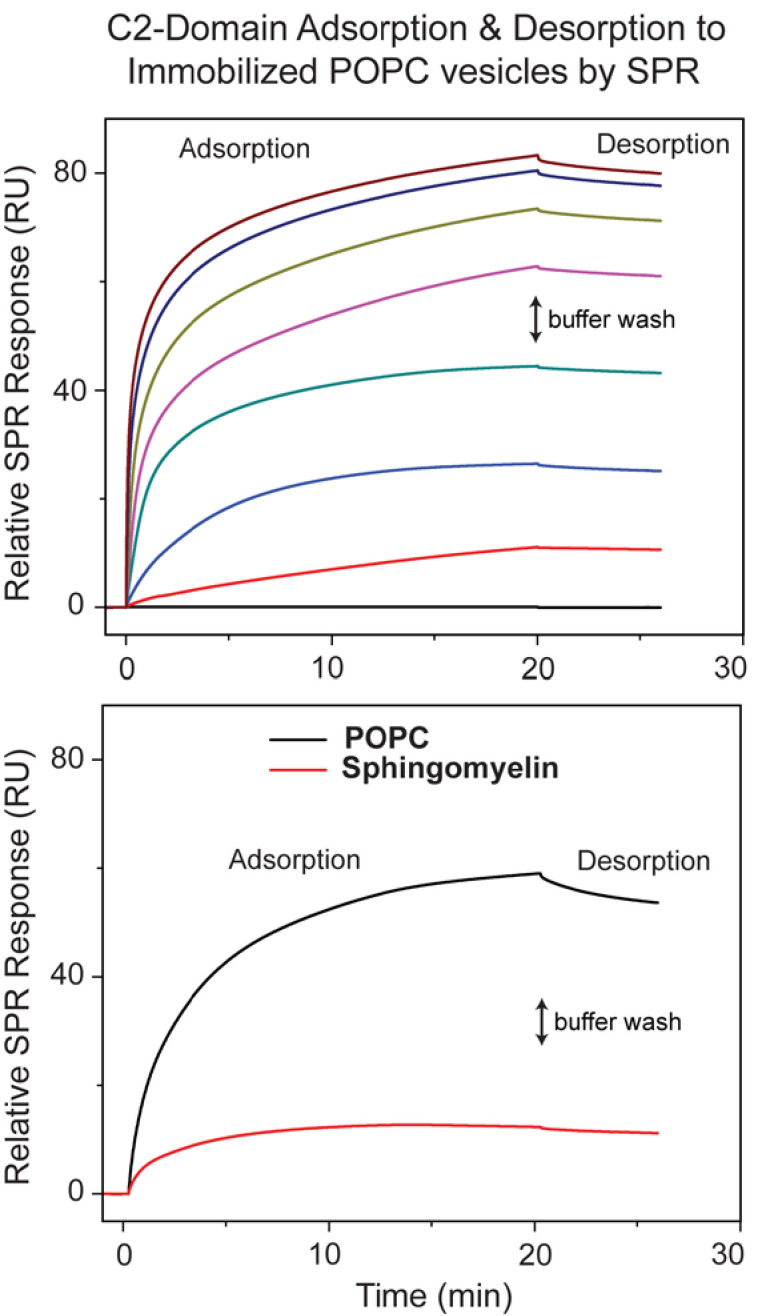
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. The concentration- and time-dependence of C2-domain adsorption/desorption to/from immobilized POPC and 18:1 SM vesicles measured by SPR.