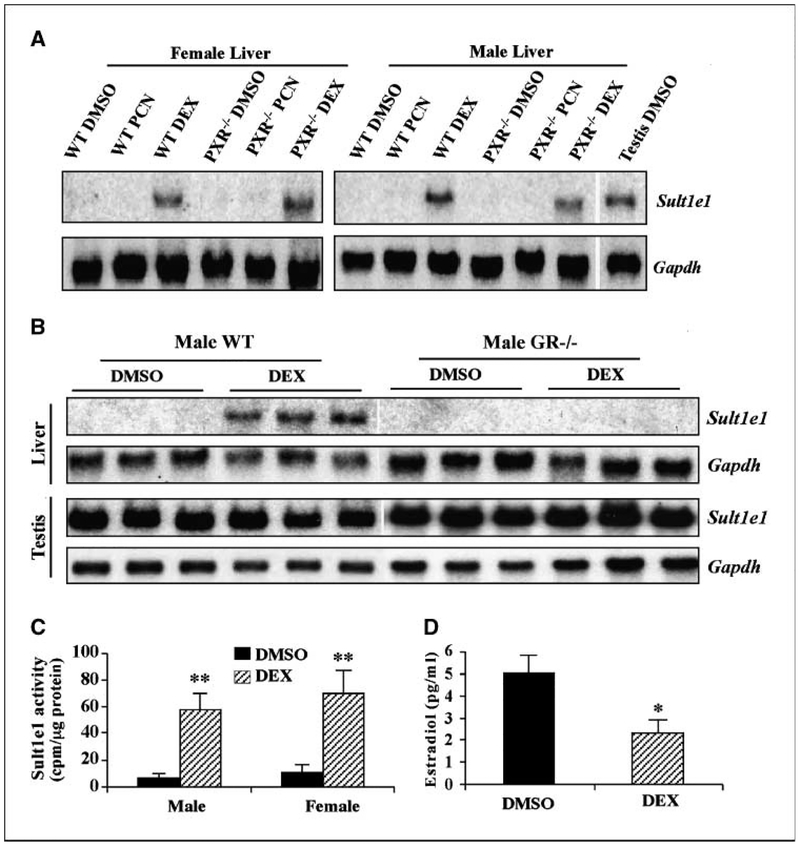
Figure 1.
Treatment with DEX induced the hepatic expression of Sult1e1 in a GR-dependent manner and decreased the circulating estrogens. A, up-regulation of hepatic Sult1e1 in the liver of wild-type mice treated with a single i.p. dose of DEX (20 mg/kg) for 24 h, as shown by Northern blot analysis. Membranes were first probed with Sult1e1 and subsequently stripped and reprobed with Gapdh as a loading control. Lanes represent individual mice. B, the effect of DEX on Sult1e1 mRNA expression is GR-dependent, as shown by Northern blot analysis. DEX treatment was the same as in A. Lanes represent individual mice. C, treatment with DEX increased estrogen sulfation. Cytosolic liver extracts from vehicle (DMSO)–treated or DEX-treated wild-type mice were subjected to sulfation assay using estrone as the substrate. [35S]PAPS was used as the sulfate donor. Radioactivity was measured by scintillation counting after separation and removal of free [35S]PAPS. D, 4-wk-old virgin wild-type female mice treated with vehicle or DEX were measured for serum estradiol levels. Mice in C and D received three daily i.p. doses of DEX (20 mg/kg) before being sacrificed. Lanes in C and D represent four to six mice per group, and results are presented as averages and SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, compared with the vehicle controls.