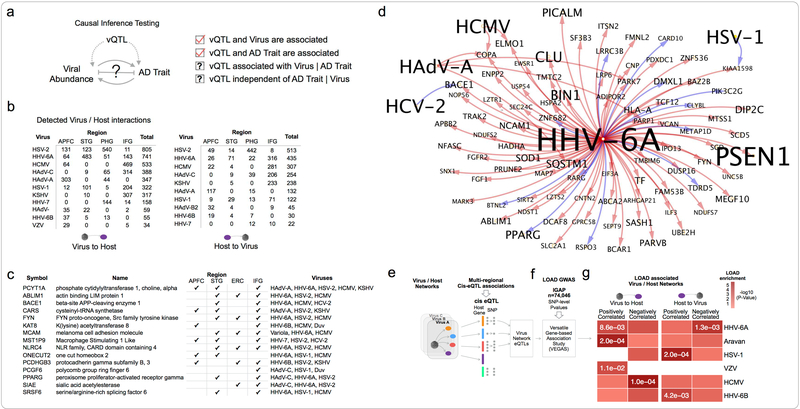
Figure 5: Viral regulation of AD associated host networks.
(a) Integration of vQTL with viral abundance, and host gene expression was used to infer directed virus / host subnetworks. (b) Virus / host gene network sizes for viruses with interactions detected in multiple tissues (c) Host genes that are most frequently perturbed by viruses (d) Host genes upregulated by HHV-6A are enriched for a heterogeneous set of AD risk and biomarker associated genes. Shown here is the HHV-6A / AD-associated gene subnetwork, and detected interactions with additional viruses. (e-g) Brain cis-eQTLs associated with expression of specific virus/host networks are enriched for AD GWAS risk loci.
(P-values shown in cells with FDR < 0.1)