Figure 5. Effects of enzyme nanoparticles of alcohol metabolism on hepatic lipogenesis and organelle stresses in mice fed chronic alcohol diet plus acute alcohol binge in the presence of anti-HIV drugs.
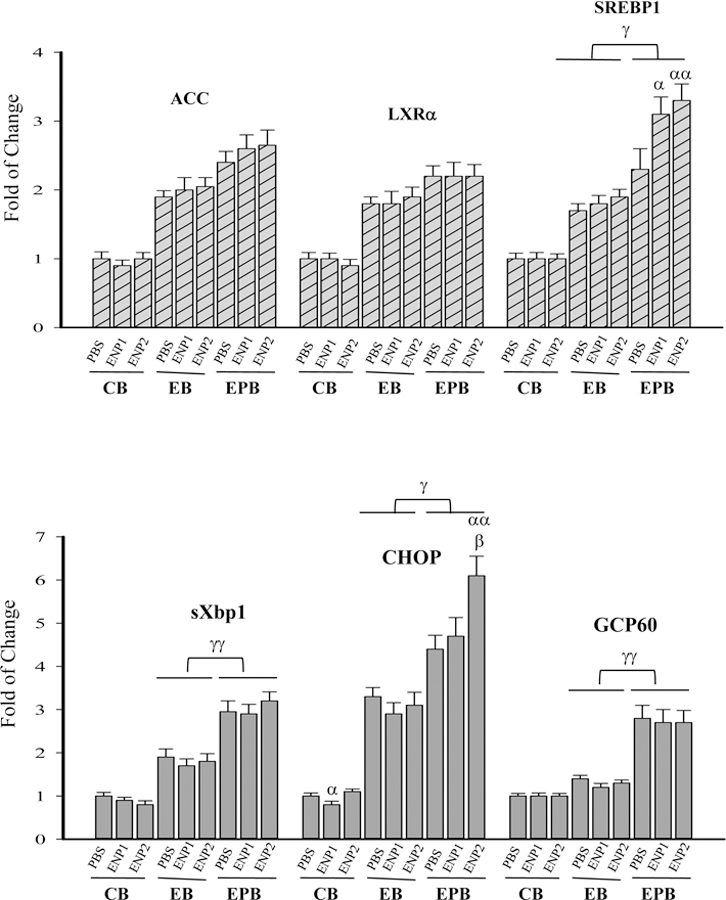

(A) Expression of lipogenic factors; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; LXRα, liver X receptor α; SREBP1c, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c; (B) Expression of selected markers for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and Golgi stress; sXbp1, the alternatively spliced form of X-box binding protein 1; CHOP, CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; GCP60, Golgi complex-associated protein 60; (C) Western blots of ER or Golgi stress related proteins; SREBP1c (p), precursor protein of SREBP1c; SREBP1c (n), nuclear or activated SREBP1c; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; ATF6 (p), precursor ATF6; ATF6 (n), nuclear or activated ATF6; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; (D) Quantitation of the activated ATF6, which was conducted with ImageJ and normalized with GAPDH; Note, the labels for all the experimental treatments are the same as those described in Figure 3. α p<0.05 and αα p<0.01 compared to PBS in the same group; β p<0.01 compared to ENP1 in the same group; γ p<0.05 and γγ p<0.01 compared between EB and EPB at the same time point; n=4.
