Fig. 4.
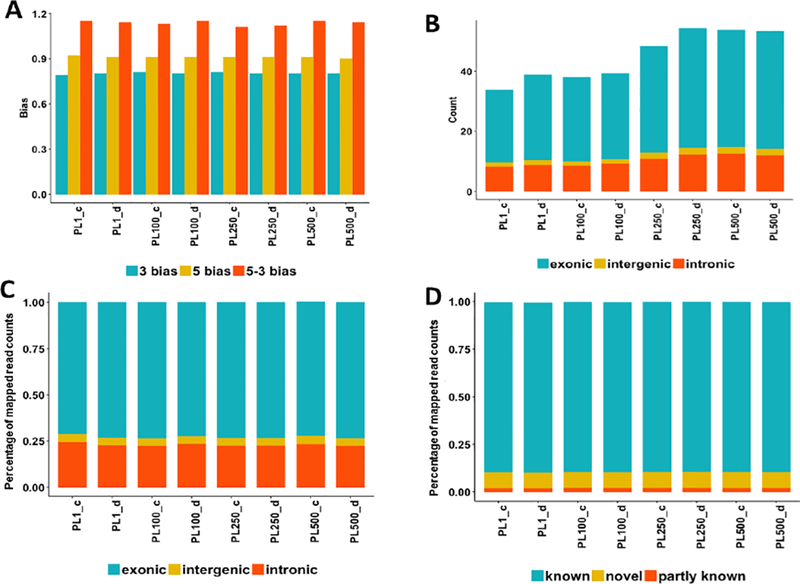
The impact of the RNA concentration on the sequencing biases in RNA-seq experiments. (A) The distribution of the 3’, 5’, and 5–3’ bias across all samples; (B) the distribution of read counts (million) in the exonic, intergenic, and intronic regions; (C) The percentage of the mapped reads within the exonic, intergenic, and intronic regions at different RNA input levels; (D) the percentage of known, novel, and partly known spliced alignments of all samples based on the Ensembl annotation (Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.gtf).
