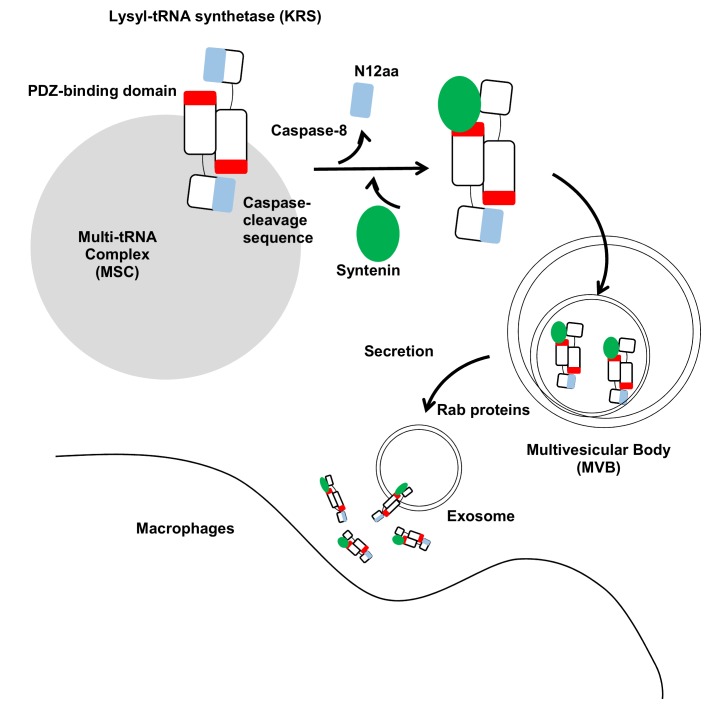
Figure 1. FIGURE 1: Schematic working model for KRS secretion.
The two KRS monomers bind in an antiparallel fashion to form a homodimer. In this dimer, the N-terminal 12 aa of KRS (blue) may block the exposure of the PDZ-binding motif located at the C-terminal end (red) in the counterpart. The starvation-induced activation of caspase-8 results in cleavage of the N-terminal 12 aa to expose the PDZ-binding motif for docking of syntenin. Syntenin (green) binding causes the dissociation of KRS from the MSC and then translocates to the exosomes in multivesicular bodies (MVBs). MVBs are translocated to the plasma membrane for exosome secretion by Rab proteins. The KRS-containing exosomes are ruptured near macrophages, releasing KRS and triggering macrophage activation and migration.