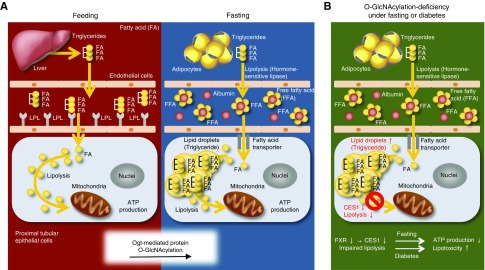
Figure 9.
Proposed hypothesis. (A) Ogt-mediated protein O-GlcNAcylation plays a critical role in maintaining renal lipolysis–dependent ATP production in proximal tubular cells during the switch from the fed to the fasting state. (B) Deficient O-GlcNAcylation impairs intracellular lipid droplet breakdown, which leads to lower ATP production during fasting and an exacerbation of intrarenal lipotoxicity in diabetes. The farnesoid X receptor (FXR)-carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) pathway may be involved in the maintenance of renal lipid metabolism, and it is regulated by O-GlcNAcylation. FA, fatty acid; FFA, free fatty acid.