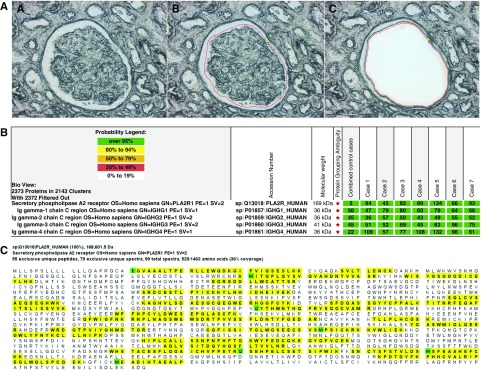
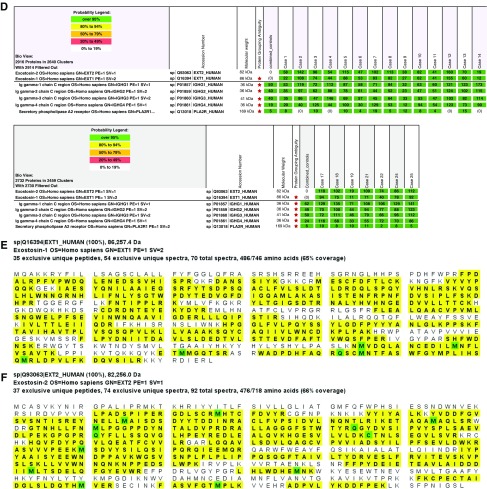
Figure 2.
Proteomic identification of PLA2R in PLA2R-associated MN and EXT1 and EXT2 in EXT1/EXT2-associated MN. Glomeruli were microdissected and analyzed using mass spectrometry as described in the Methods section. (A) Laser microdissection of glomeruli. One case of MN showing (A) unmarked glomerulus, (B) glomerulus marked for dissection, and (C) vacant space on the slide after microdissection. (B) PLA2R-associated MN: Protein identification report from seven cases is shown. Numbers in green boxes represent spectral counts of MS/MS matches to a respective protein. All seven cases show large total spectral counts for PLA2R and Ig. For comparison, the average total spectral counts from six control cases (day 0 protocol transplant biopsy specimens) are also shown. (C) Representative sequence coverage map of PLA2R from one case. Amino acids highlighted in bold letters over yellow background are the amino acids detected. Note the extensive coverage. Green highlighted boxes indicate amino acids with artifactual chemical modification induced by mass spectrometry such as oxidation of methionine. (D) EXT1/EXT2-associated MN: Protein identification from all 21 cases showing total spectral counts for both EXT1 and EXT2. For comparison, the average total spectral counts in six control cases (day 0 protocol transplant biopsy specimens) are also shown. IgG1 was the dominant IgG present. Higher spectral IgG counts in the control cases in the bottom panel compared with the top panel reflect normalization, with fewer EXT1/EXT2 cases in the lower panel compared with the top panel. (E and F) Sequence coverage maps: Representative EXT1 and EXT2 sequence coverage map from a case of EXT1/EXT2-associated MN showing the extensive amino coverage of both (E) EXT1 and (F) EXT2 by MS/MS. Amino acids highlighted in bold letters over yellow background are the amino acids detected. Note the extensive coverage. Green highlighted boxes indicate amino acids with artifactual chemical modification induced by mass spectrometry such as oxidation of methionine.