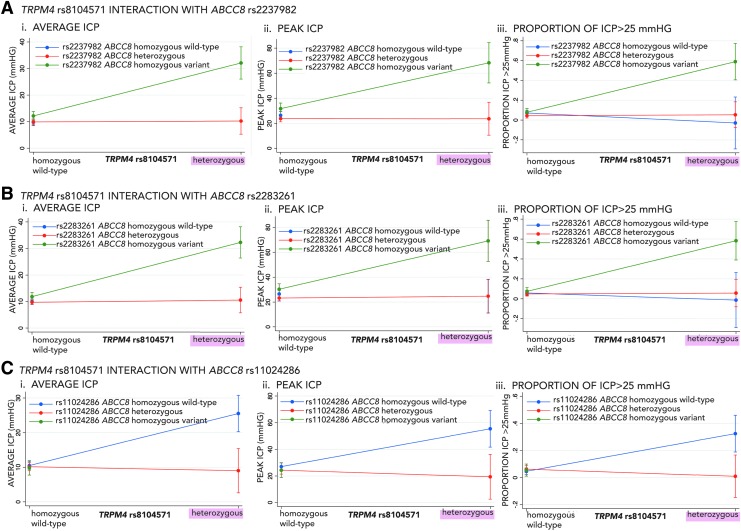
FIG. 3.
Interaction effects of transient-receptor-potential cation channel subfamily-M (TRPM4) rs8104571 with previously reported significant ABCC8 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on intracranial pressure (ICP). Graphs demonstrating the direction and magnitude of the interaction effect on ICP between TRPM4 rs8104571and each of the three ABCC8 SNPs previously implicated as significant in traumatic brain injury (TBI) organized into the following panels: (A) ABCC8- rs2237982, (B) ABCC8-rs2283261, and (C) ABCC8-rs11024286. Panel subgraphs show the interaction effects between these SNPs on various measures of ICP including (i) average-ICP, (ii) peak = ICP, and (iii) proportion of ICP spikes >25 mm Hg. The x axes for all graphs are TRPM4 rs8104571 genotypes: homozygous wild-type and heterozygous. The y axes for subgraphs A-i, B-I, and C-i are average ICP (mm Hg). The y axes for subgraphs A-ii, B-ii, and C-ii are peak ICP (mm Hg). The y axes for subgraphs A-iii, B-iii, and C-iii are proportion of ICP >25 mm Hg. Each individual graph shows the interaction between TRPM4 rs8104571 genotypes and the respective ABCC8 SNP genotypes where homozygous wild-type ABCC8 genotypes are in blue, heterozygous ABCC8 genotypes are in red, and homozygous-variant ABCC8 genotypes are in green. Error bars are 95% confidence intervals. For example, in Panel A-subgraph i, the average ICP in patients who are homozygous-wild type for TRPM4 rs8104571 is ∼10 mm Hg regardless of the ABCC8 rs2237982 genotype. However, in patients heterozygous for TRPM4 rs8104571, the average ICP is significantly higher (i.e., ∼30 mm Hg) if the patients are also homozygous-variant for ABCC8 rs2237982. In panels A-i, A-ii, B-i, and B-ii (depicting interaction effects on average and peak ICP), there are no observations for homozygous wild-type ABCC8 SNPs (blue) in any of these panels, because the interaction coefficient was omitted by the regression model as a result of collinearity between heterozygous TRPM4 rs8104571 and homozygous wild type ABCC8 rs2237982 (A-i, A-ii) as well as between TRPM4 rs8104571 and homozygous wild-type ABCC8 rs2283261 (B-i, B-ii). For Panel C (i, ii, iii) there were no patients who were both heterozygous for TRPM4 rs8104571 and homozygous variant for ABCC8 rs11024286.