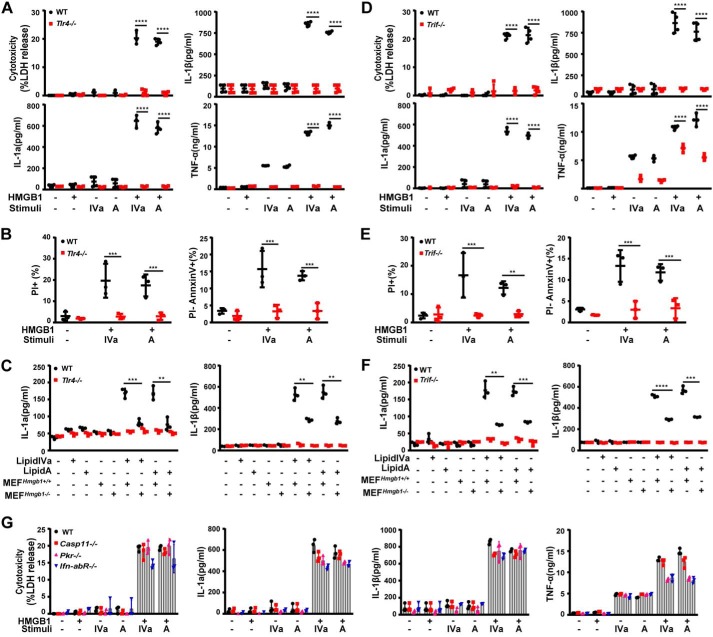
Figure 3.
TLR4-TRIF signaling mediates HMGB1/microbial lipid-induced proinflammatory cell death. A and D, LDH, IL-1α, IL-1β, and TNFα were measured from culture supernatants of peritoneal macrophages from WT and Tlr4−/− or TrifLps/Lps2 mice stimulated with lipid IVa or lipid A (1 μg/ml) in the absence or presence of HMGB1 (0.4 μg/ml). B and E, flow cytometry analysis of the percentage of WT and Tlr4−/− or TrifLps/Lps2 macrophages undergoing necrosis (PI+) or apoptosis (PI−) after stimulation with lipid IVa or lipid A (1 μg/ml) in the presence of HMGB1 (0.4 μg/ml). C and F, IL-1α and IL-1β measured from the supernatants of peritoneal macrophages from WT and Tlr4−/− or TrifLps/Lps2 mice upon exposure to necrotic Hmgb1−/− or Hmgb1+/+ MEF in the presence or absence of lipid IVa or lipid A (1 μg/ml). G, LDH, IL-1α, IL-1β, and TNFα measured from culture supernatants of peritoneal macrophages from mice with the indicated genotypes after stimulation with lipid IVa or lipid A (1 μg/ml) in the absence or presence of HMGB1 (0.4 μg/ml). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Graphs show the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments.