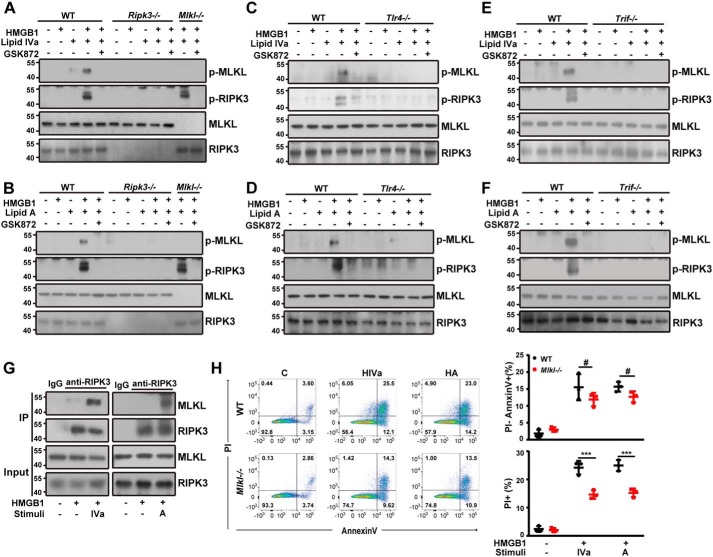
Figure 4.
TLR4-TRIF-RIPK3 signaling mediates MLKL-dependent necroptosis induced by HMGB1 and microbial lipids. A and B, Western blot analysis of phosphorylated MLKL and RIPK3 in peritoneal macrophages from WT, Ripk3−/−, and Mlkl−/− mice exposed to the indicated stimuli in the absence or presence of GSK872. C and D, Western blot analysis of phosphorylated MLKL and RIPK3 in peritoneal macrophages from WT and Tlr4−/− mice exposed to the indicated stimuli in the absence or presence of GSK872. E and F, Western blot analysis of phosphorylated MLKL and RIPK3 in peritoneal macrophages from WT and TrifLps/Lps2 mice exposed to the indicated stimuli in the absence or presence of GSK872. G, cell lysates of peritoneal macrophages from a WT mouse treated with the indicated stimuli were immunoprecipitated (IP) with RIPK3-specific antibody. The precipitated proteins were immunoblotted with RIPK3- or MLKL-specific antibodies. Whole cell lysate (Input) was used as positive control. H, flow cytometry analysis of the percentage of WT or Mlkl−/− peritoneal macrophages undergoing necrosis (PI+) or apoptosis (PI−) following stimulation with lipid IVa or lipid A (1 μg/ml) in the presence of HMGB1 (0.4 μg/ml). ***, p < 0.001; #, not significant. Graphs show the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments.