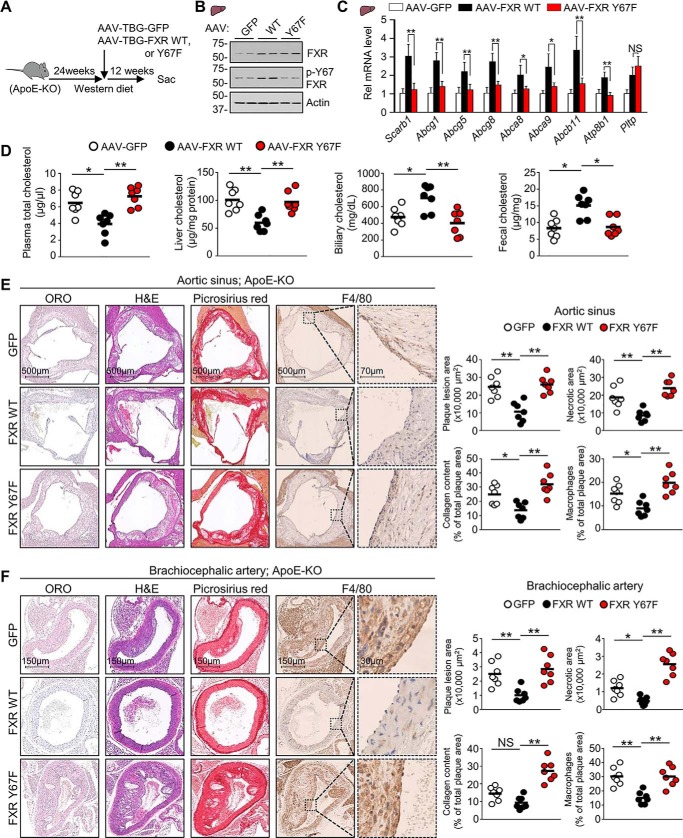
Figure 4.
Atheroprotective effects by hepatic FXR in ApoE-KO mice are diminished by the p-defective Y67F mutation. ApoE-KO mice that had been fed a Western diet for 24 weeks were infected with AAV-TBG-GFP or AAV-TBG expressing WT-FXR or Y67F-FXR (7 mice/group), and feeding of the Western diet continued until sacrifice 12 weeks later. A, experimental outline. B, protein levels of FXR, p-Y67-FXR, and actin in liver extracts were determined by IB. C, the mRNA levels of the indicated genes were measured by RT-qPCR (n = 7). D, cholesterol levels in the plasma, liver, gallbladder, and feces (n = 7). E and F, from the left image panel to the right image panel, representative cross-sections of Oil Red O staining for atherosclerotic lesions, H&E staining for necrotic core detection, Picrosirius red staining of collagen (red), and immunohistochemical staining with anti-macrophage (F4/80) antibody to detect macrophages (brown) for the aortic sinus (E) or the brachiocephalic artery (F). Right, quantification of plaques, necrotic core, collagen content, and macrophages for the aortic sinus (E) or brachiocephalic artery (F). C, all values are presented as mean ± S.D. (error bars). D–F, a horizontal line indicates the mean in the graphs. C–F, statistical significance was measured using the one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post-test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; NS, statistically not significant.