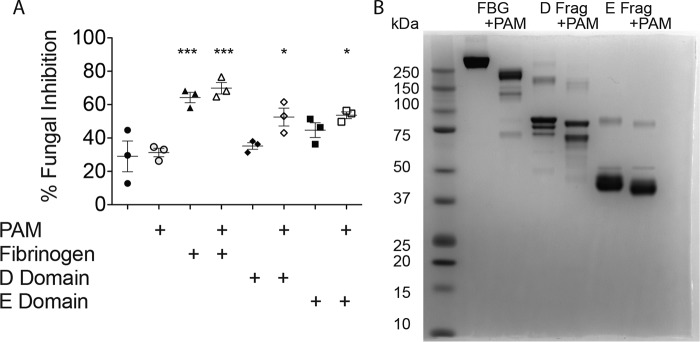
Figure 5.
Fibrinogen D and E fragments are sufficient substrates through which PAM can generate functional FCPs. A, fungistasis assays were performed that compared PAM-induced FCPs derived from whole-human fibrinogen, the fibrinogen D fragment, and the fibrinogen E fragment as indicated using murine splenocytes. All fibrinogen moieties were added at the same concentration (100 nm). B, nonreducing SDS-PAGE analysis of native proteins and PAM–FCPs derived from whole FBG, and the D and E fragments (Frag) of fibrinogen. n = 3 biologic replicates per group. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test of fragments and FCPs compared with blank and PAM controls. Statistical data are representative of at least two similar, independent experiments.