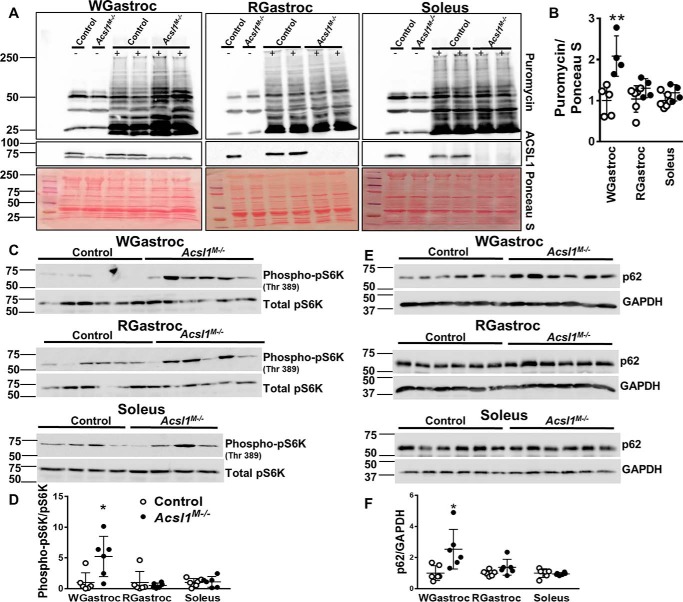
Figure 8.
Deletion of Acsl1 increased protein synthesis in glycolytic muscle after endurance exercise. Mice were exercised on a treadmill for 45 min, and sterilized puromycin solution in water (0.04 μmol/g) was injected IP immediately afterward. White gastrocnemius (WGastroc), red gastrocnemius (RGastroc), and soleus were collected 30 min later and homogenized. Homogenates were then probed with anti-puromycin and anti-ACSL1 antibodies. ImageJ software was used to quantify relative pixel density of the bands. A, representative Western blots of anti-puromycin and anti-ACSL1 (−, no puromycin injection; +, puromycin injection), and membranes were stained with Ponceau S. B, quantitation of puromycin incorporation normalized to Ponceau S, n = 4–5 per genotype. C, Western blots of anti-phospho-pS6K and anti-total pS6K in white gastrocnemius and red gastrocnemius. Representative Western blotting of anti-phospho-pS6K and anti-total pS6K in soleus. D, quantitation of pS6K phosphorylation, n = 6 per genotype. E, Western blots of anti-p62 and anti-GAPDH in white gastrocnemius, red gastrocnemius, and soleus. F, quantitation of p62 was normalized to GAPDH, n = 6 per genotype. Data are presented as means ± S.D. (error bars). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.