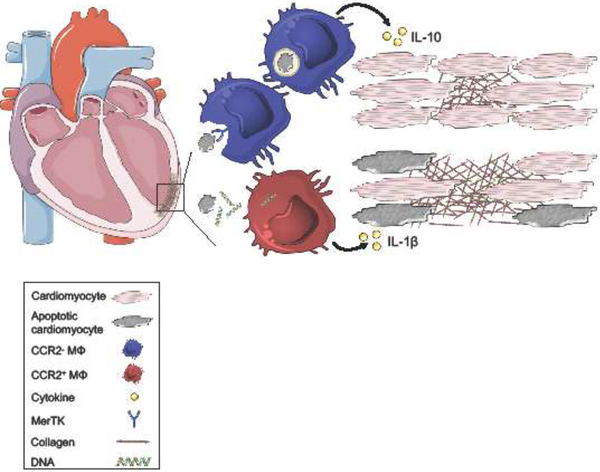
Figure 2. The balance of macrophage inflammatory and reparative responses sets the clinical trajectory in HFrEF.
Following myocardial infarction, cardiomyocyte death primarily occurs through apoptosis and necrosis. Macrophages express surface receptors, including MER proto-oncogene Tyrosine Kinase (MerTK), that recognize and mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Engulfment and metabolism of dying cells stimulates macrophage production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10, which preserves neighboring tissue and cardiac function. Dying cardiomyocytes also secrete damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMP), including double-stranded DNA. Macrophage recognition of DAMPs promotes secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β leading to collateral tissue damage, adverse ventricular remodeling, and systolic dysfunction.