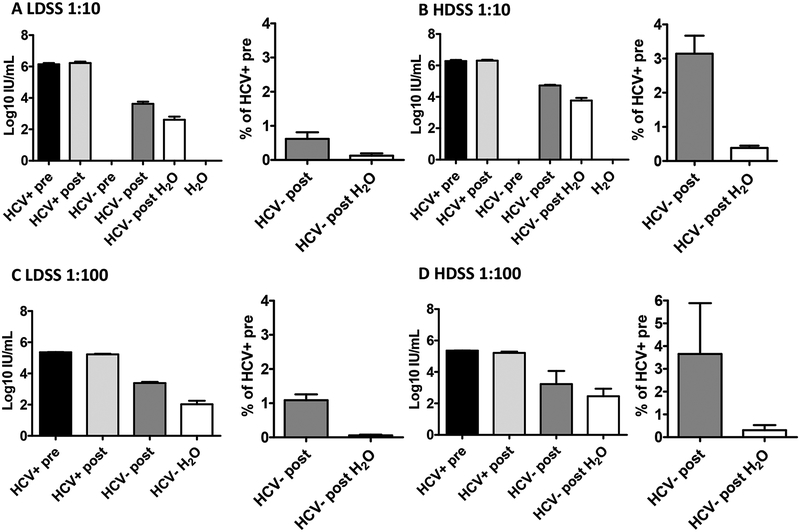
Fig. 2. RNA carry-over of HCV Positive Human Plasma in two different syringe types with attached needles.
Mean RNA titers and percentage carry-over for HCV-positive human plasma samples (diluted 1:10) after being carried over in (A) low dead space syringes (LDSS) and (B) high dead space syringes (HDSS) (mean of 3 independent experiments). Mean RNA titers and percentage carry-over for human plasma samples (diluted 1:100) after being carried over in (C) low dead space syringes and (D) high dead space syringes (mean of 3 independent experiments). Bars represent s.e.m. Means were calculated using log-transformed data. HCV+ pre= HCV-positive plasma before uptake into a syringe; HCV+ post= HCV-positive plasma after expulsion from the syringe; HCV- pre= HCV-negative plasma before uptake into a syringe; HCV- post= HCV-negative plasma after uptake and expulsion from a contaminated syringe; HCV- post H2O= HCV-negative plasma after uptake and expulsion from a contaminated syringe rinsed in tap water.