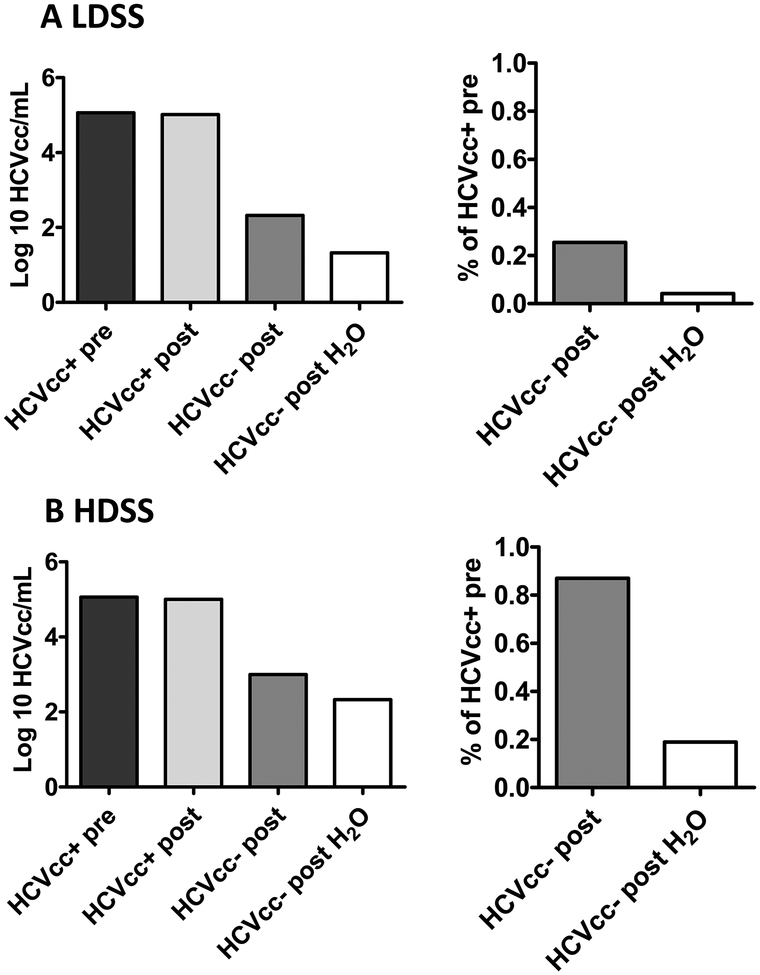
Fig. 3. Carry-over of HCV cell culture virus (HCVcc) positive samples in two different syringe types with attached needles.
Shown are mean titers and percentage carry-over of HCVcc before uptake into (A) a low dead space syringe (LDSS) (B) a high dead space syringe (HDSS). HCVcc+ pre= HCVcc-positive sample before uptake into a syringe; HCVcc+ post= HCVcc-positive sample after expulsion from the syringe; HCVcc- post= HCVcc-negative plasma after uptake and expulsion from a contaminated syringe; HCVcc- post H2O= HCVcc-negative plasma after uptake and expulsion from a contaminated syringe rinsed in tap water. Data represent the mean values of 2 independent experiments. Percentages were calculated as described for Figure 2 using HCVcc titers instead of HCV RNA titers. Means were calculated using log transformed data. Ranges taken from all experiments are reported in the text.