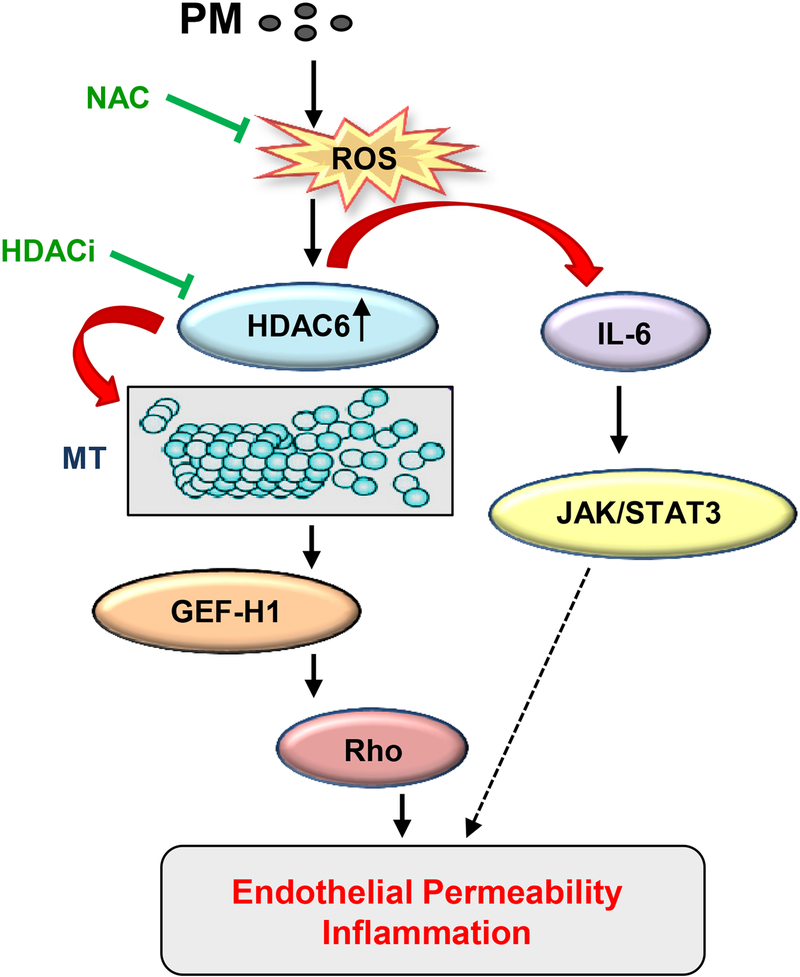
Figure 6. Proposed mechanisms of PM-induced EC dysfunction via MT destabilization.
PM induces ROS generation leading to oxidative HDAC6 activation which in turn destabilizes MT by deacetylation of a-tubulin within stable microtubules. MT depolymerization causes release of MT-bound GEF-H1 and subsequent activation of the Rho pathway. Simultaneously, PM-induced HDAC6 activation via positive feedback regulation of ROS production stimulates IL-6 expression and activation of JAK-STAT3 pathway of EC inflammation and barrier dysfunction. Both these signaling events ultimately result in increased EC permeability and inflammation.