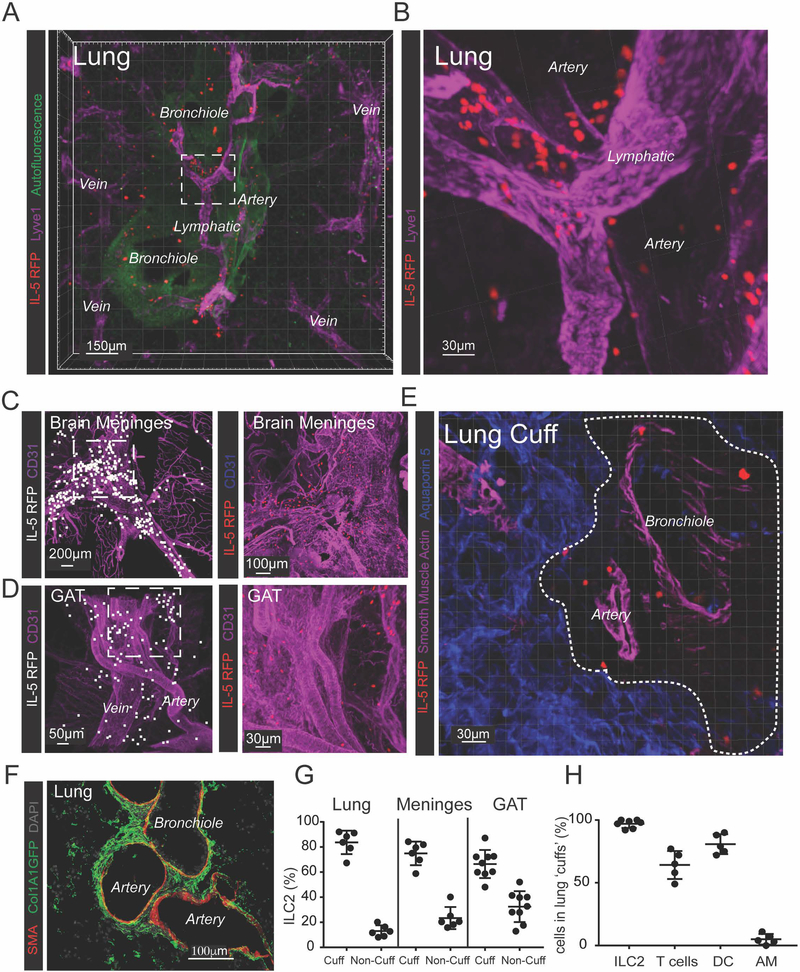
Figure 1: ILC2s localize to adventitial cuffs in multiple organs.
(A and B) 3D rendering with zoom of a 200μm thick lung slice with IL-5+ ILC2 (RFP), bronchioles (autofluor+ Lyve−), arteries (Lyve1dim+, Autofluor+, bronchiole−adjacent), veins (Lyve1dim+ Autofluor+, non-bronchiole adjacent) and lymphatics (Lyve1bright+, Autofluor−) visualized. (C and D) IL-5 RFP+ ILC2 and CD31+ vessels visualized in (C) brain meninges and (D) perigonadal adipose tissue (GAT). (E and F) IL-5 RFP+ ILC2 visualized in the lung adventitial cuff, highlighted by a lack of (E) Aquaporin 5 and SMA, and positively by (F) Col1A1 rich cuff regions surrounding bronchioles and arteries. (G) 3D image quantification of IL-5 RFP+ ILC2s localized within the cuff volume, using automatic surfacing (lungs), or found within 40μm of SMA+ vasculature (meninges, GAT). (H) Percent of cells in lung cuffs: ILC2 (IL-5 RFP+), T-cells (CD3ε+), DCs (CD11c+ MHCII+ co-positive) and alveolar macrophages (AM, CD11c+ MHCII−). Analysis in (G) included lung cuff, parenchyma, and pleural regions, whereas (H) excluded pleura. (A-E) Images are representative of 3 or more mice or (F) 2 mice. (G and H) Data points represent averages of individual mice with n ≥5 animals with ≥55 cells of each type analyzed per mouse. See also Figures S1–3 and Movies S1 and S2.