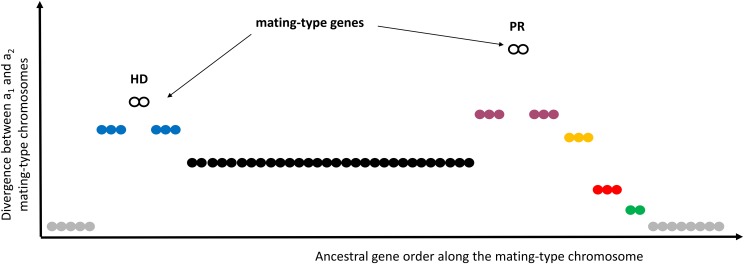
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the evolutionary strata on the mating-type chromosome of Microbotryum lychnidis-dioicae. The per-gene synonymous divergence between alleles (y-axis) represents relative timing of the suppression of recombination steps plotted along the ancestral gene order (x-axis). The PR and HD gene clusters (open black circles) show the most ancient divergences. They control pre- and post-mating compatibility, respectively, and encompass several ancestrally linked mating-type genes. The sequence of suppression of recombination begins around each of the mating-type loci, generating the blue and purple evolutionary strata. Recombination suppression then spread distally to the PR locus, creating the orange stratum. The event that linked the two mating-type loci and their surrounding strata generated the black stratum. The suppression of recombination then spread further outwards distal to the PR locus, creating the red and then the green strata. The pseudo-autosomal regions, which are still recombining, are shown in gray. Only the evolutionary strata shown in black (open or closed black circles) involve linking mating-type genes.