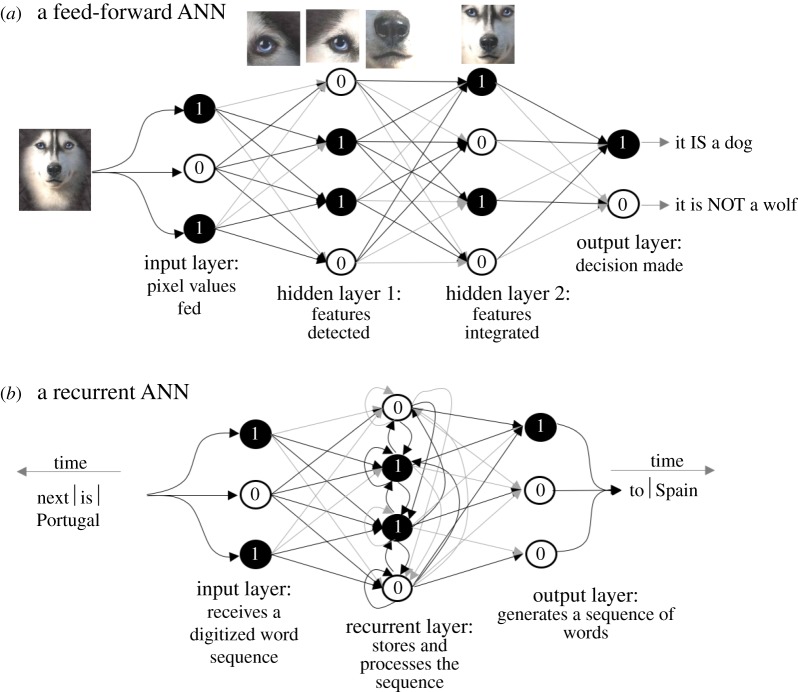
Figure 4.
The two main types of artificial neural networks (ANNs). Schematics of ANNs, with the arrows representing connections between neurons, and the numbers 1 and 0 representing the possible binary states of the neurons (processing units). The grey level of the edges represents the associated weights. Panels show schematics of possible mechanisms by which: (a) a feed-forward ANN might distinguish huskies from wolves; and (b) a recurrent ANN might predict meaningful sequences of words from an input sequence. (Online version in colour.)