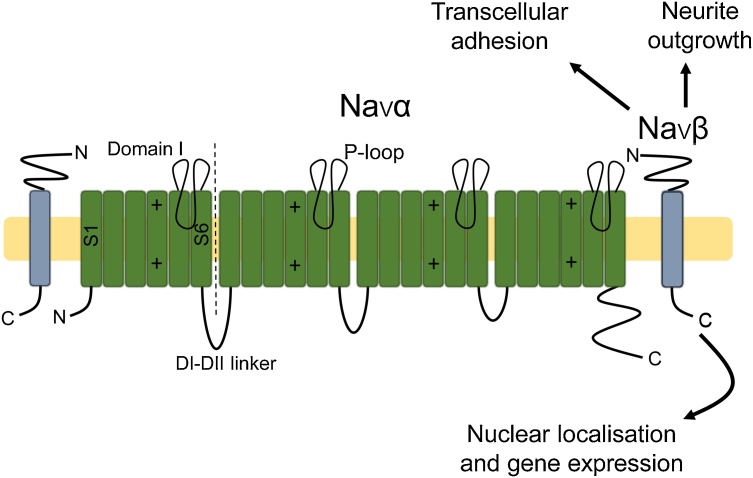
Fig. 3.
Voltage-gated Na+ channel auxiliary subunits. Voltage-gated Na+ channels (VGSCs) contain a conducting Navα subunit and auxiliary Navβ subunits. Navα consists of four domains (domains I-IV), each containing six segments (S1-S6). The voltage-sensing domain is found within S4 of each domain and the pore consists of the P-loop found between S5-6 of each domain. Navβs function as cell adhesion molecules via an extracellular immunoglobulin domain [238,239,332]. Navβs also induce neurite outgrowth and migration [245] and the intracellular domain of Navβ2 has putative transcription regulation function [248].