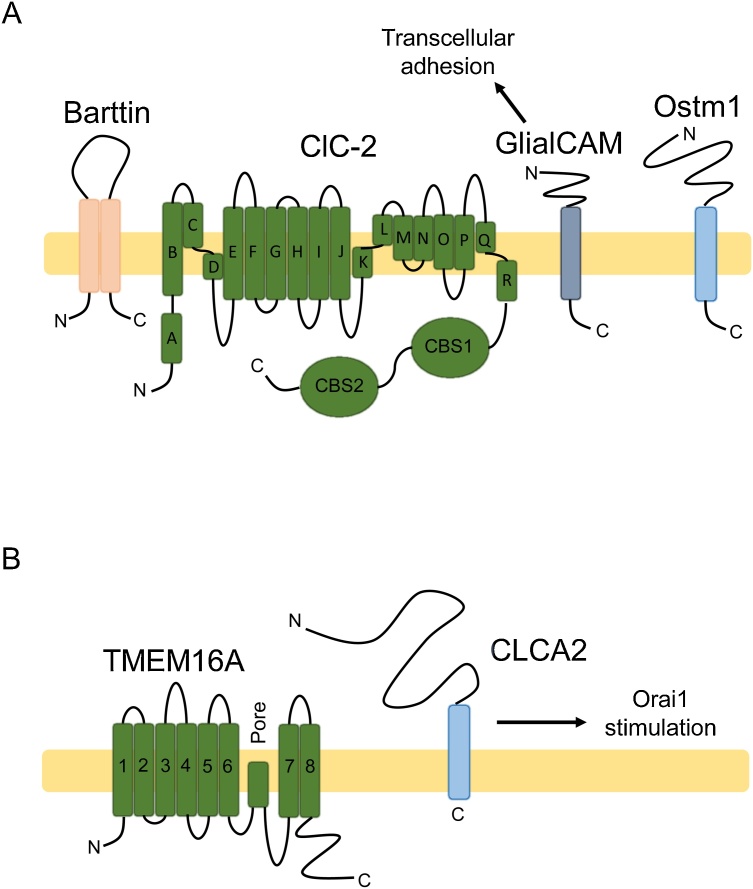
Fig. 4.
Cl− channel auxiliary subunits. (A) CLCs are a subfamily of voltage-sensitive Cl− channels and transporters found at the plasma membrane and internal membranes [13]. Barttin modulates ClC-K, GlialCAM modulates ClC-2 and Ostm1 modulates the intracellular ClC-7 transporter [264,266,267]. CLCs are composed of eighteen helical domains and two C-terminal cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) domains which facilitate dimerization [333]. Depicted is the plasma membrane ClC-2 which interacts with single-pass GlialCAM, the only ClC auxiliary subunit implicated in cancer [264]. GlialCAM can also function as a cell adhesion molecule [268]. (B) Two separate CaCC conducting subunits exist- TMEM16 and Bestrophin. Depicted is eight-pass TMEM16 A which is modulated directly by secreted CLCA1 and indirectly by single-pass CLCA2 [303,305]. CLCA2 stimulates Ca2+ store replenishment by interacting with Orai1 and STIM1 [305].