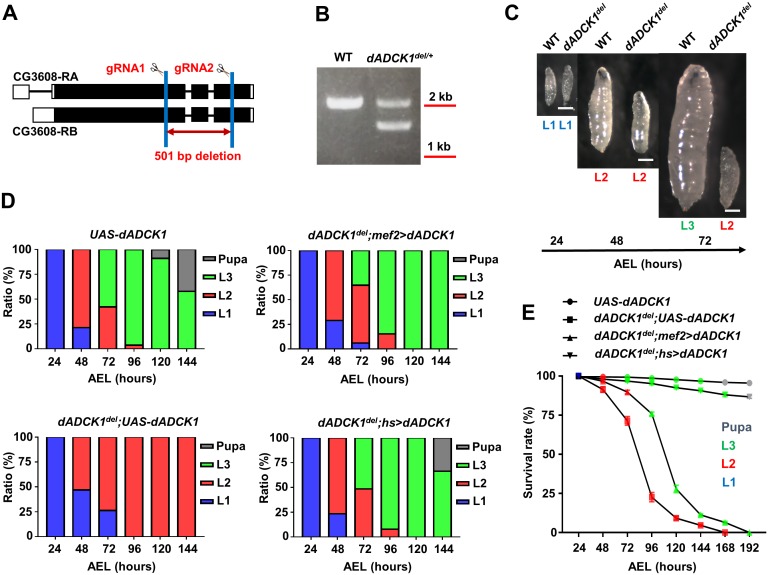
Fig 1. ADCK1 mutant flies show development defects.
(A) A scheme to generate a dADCK1 deletion allele (dADCK1del) by CRISPR/Cas9. (B) A DNA gel electrophoresis result for the genomic DNA of wild type (WT) and heterozygous dADCK1 mutant allele (dADCK1del/+). (C) Comparison of the body size and developmental stages between WT (left) and dADCK1del (right) flies. WT flies were first instar (L1), second instar (L2), and third instar (L3) larvae at 24, 48, and 72 hours after egg laying (AEL), respectively. dADCK1del flies in these photos were first instar and second instar larvae, collected at the same time points. Scale bars, 0.1 mm. (D) Developmental progression of the flies with indicated genotypes. n = 375~403. (E) Comparison of the viability of the flies with indicated genotypes. n = 375~403. Statistical significance was analyzed by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. p<0.0001. Color-coded symbols indicate specific developmental stages.