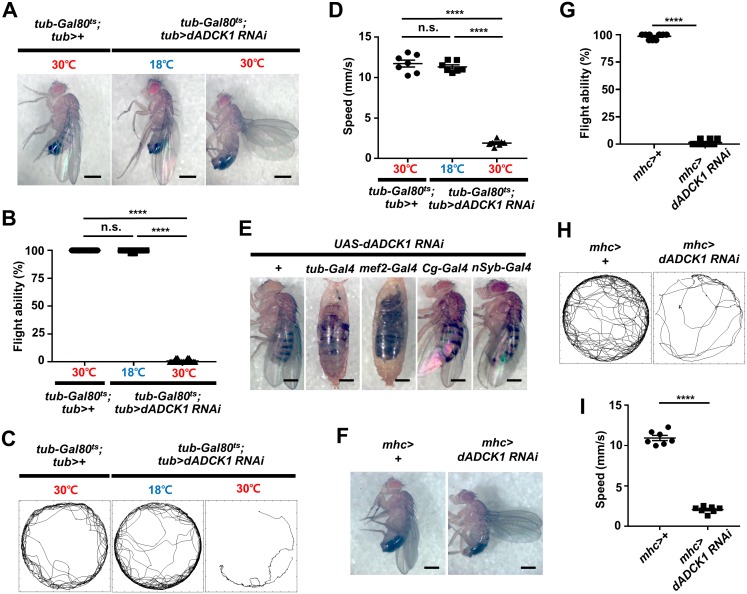
Fig 2. ADCK1 knockdown causes abnormality in locomotive activity.
(A) Whole body images of the adult flies with indicated genotypes raised at noted temperatures. Scale bars, 0.5 mm. (B) Comparison of the flight ability for the flies with indicated genotypes. n = 20. ****, p<0.0001; n.s., not significant by unpaired t-test. (C) Movement trajectories of the adult flies with indicated genotypes and raised temperatures. (D) Comparison of the means of walking speed for the flies with indicated genotypes, n = 7. ****, p<0.0001; n.s., not significant by unpaired t-test. (E) Whole body images of the flies with indicated genotypes. dADCK1 knockdown using ubiquitous tub-Gal4 driver, muscle-specific mef2-Gal4 driver, fat body-specific Cg-Gal4 driver, and neuron-specific nSyb-Gal4 driver. Scale bars, 0.5 mm. (F) Whole body images of the adult flies with indicated genotypes. Scale bars, 0.5 mm. (G) Comparison of the flight ability for the flies with indicated genotypes. n = 10. ****, p<0.0001 by unpaired t-test. (H) Movement trajectories of the adult flies with indicated genotypes. (I) Comparison of the means of walking speed for the flies with indicated genotypes, n = 7. ****, p<0.0001 by unpaired t-test.