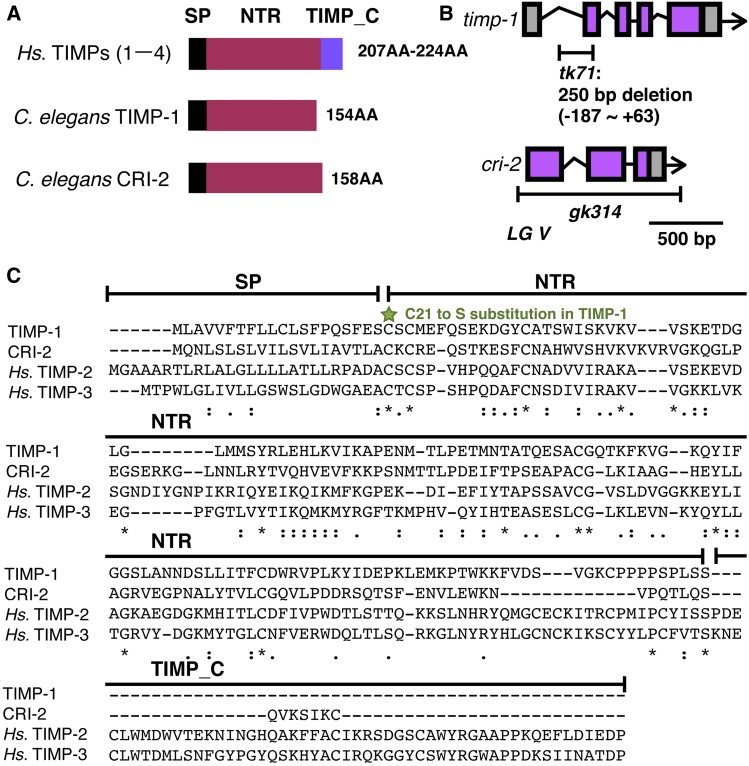
Figure 1.
C. elegans TIMP genes (A) Domain structures of H. sapiens TIMPs, and C. elegans TIMP-1 and CRI-2. (B) Genomic structures and deletion sites in timp-1 and cri-2. In tk71, nucleotides between positions −187 and +63 in the TIMP-1 gene are deleted. The gk314 mutation is a complete deletion of the cri-2 coding region. (C) Multiple sequence alignment of the TIMP-1, CRI-2, and Hs. TIMP-2 and -3 precursors. The green star indicates the C21S mutation site in TIMP-1. Asterisks indicate positions at which a residue is fully conserved. Colons indicate positions at which residues have very similar physical properties (score > 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). Periods indicate positions at which residues have weakly similar physical and chemical properties (score ≤ 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). Hs., H. sapiens; NTR, netrin-like domain; PAM, point accepted mutation; SP, signal peptide; TIMPs, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases; TIMP_C, TIMP C-terminal domain.