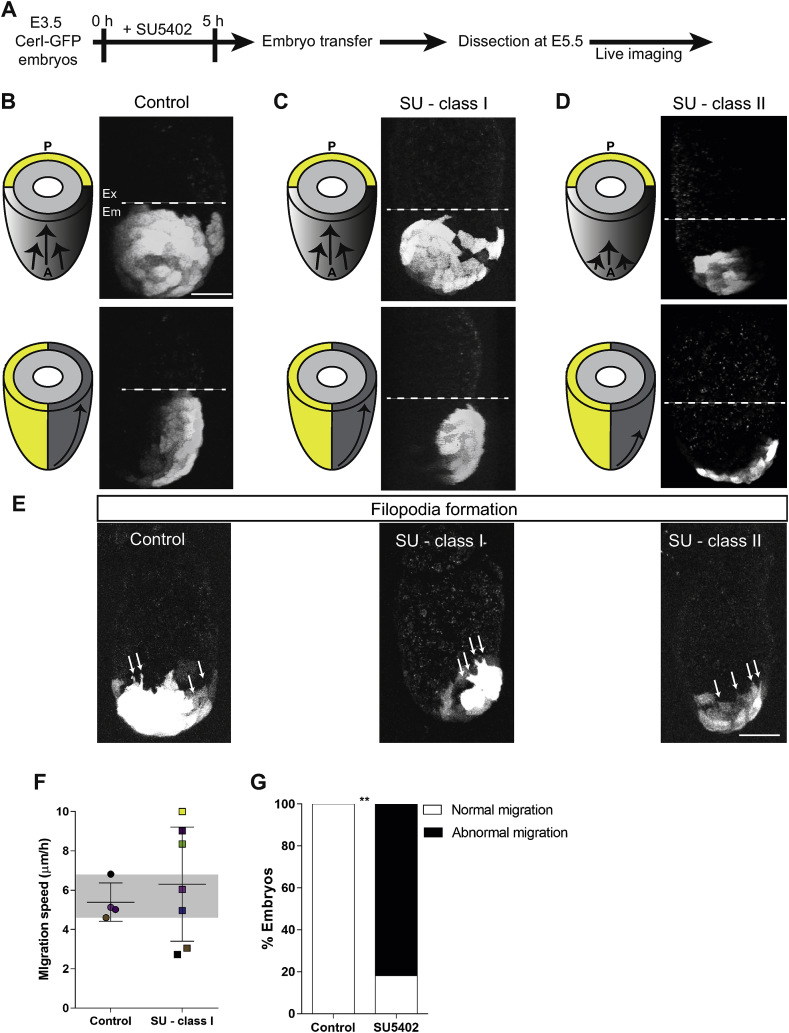
Fig. 4.
FGF signalling-mediated perturbation of cell cycle affects post-implantation morphogenesis (A) Schematic view of the experimental design: E3.5 Cerl-GFP embryos were treated with SU5402 for 5 h and then transferred to foster mothers. Embryos were recovered at E5.5 and live imaged. (B–D) Anterior view (top panels) and lateral view (bottom panels) of migrated AVE in Cerl-GFP embryos. Embryos were divided based on the phenotype in control (B) and SU5402 treated embryos class I (SU - class I) (C) or class II (SU - class II). (D) (Scale bar = 50 μm). (E) Filopodia in migrating CerI-GFP+ cells showed in control (left panel) and SU5402 treated embryos class I (middle panel) or class II (left panel). Arrows indicate filopodia. (Scale bar = 50 μm). (F) AVE migration speed shown as μm/h in control or SU – class I embryos. Data are shown as mean ± sd (Unpaired t-test, ns). The grey band represents the interdecile range (ID) calculated on the control values: 10% Percentile = 4.6 and 90% Percentile = 6.8. (G) Percentage of control or SU5402-treated embryos (class I and class II) showing normal or abnormal AVE migration in control (n = 4) or SU5402-treated embryos (n = 11) (χ2 test, **p = 0.0042).