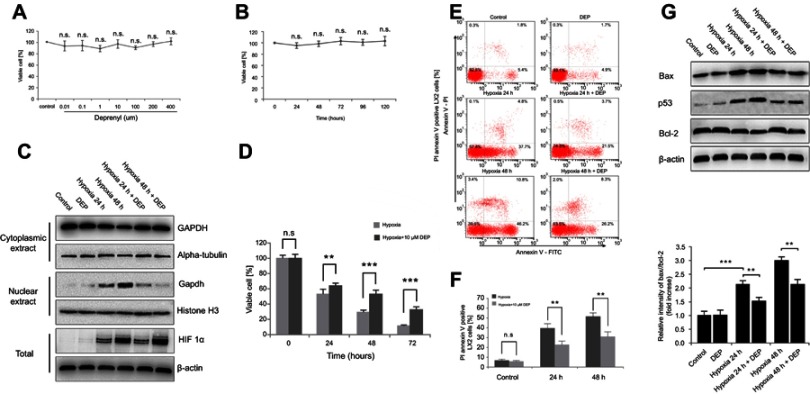
Figure 2.
Deprenyl inhibits the hypoxia-induced nuclear translocation of GAPDH and protects LX2 cells from apoptosis. (A and B) Deprenyl toxicity was detected using the MTT assay. LX2 cells were exposed to different concentrations of deprenyl for 48 hrs (A) or to 10 µM deprenyl for different times (B). LX2 cells were exposed to hypoxia for different periods after preincubation with 10 µM deprenyl. (C) The effect of deprenyl on hypoxia-induced nuclear GAPDH accumulation. (D) Cell viability was measured using the MTT assay. (E and F) Cell apoptosis was detected using annexin V-FITC/PI double staining and flow cytometry (E), and bar graphs (F) show the effect of deprenyl on apoptosis. (G) The effect of deprenyl on the levels of apoptotic proteins in LX2 cells. Untreated samples served as controls.
Note: Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n.s., not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, n=3.
Abbreviations: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DEP, deprenyl.