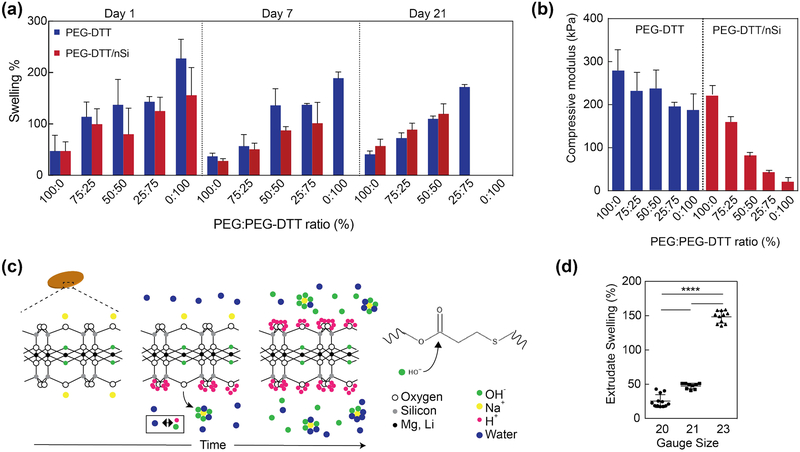
Figure 3.
Swelling and degradation of crosslinked nanocomposite hydrogels. (a) Swelling of covalently crosslinked PEGDTT and PEGDTT/nSi hydrogels was monitored over 21 days. The dimensions of the sample used for swelling and degradation studies were 1 mm thick × 5 mm diameter. The ratio of PEG:PEGDTT was modulated to control the physiochemical characteristics of hydrogels (n=5). (b) Effect of PEG:PEGDTT ratio and addition of nanosilicate (4% wt/vol)) on compressive properties of crosslinked hydrogel. PEG:PEGDTT was constant at 10% wt/vol of the solution (n=5). (c) Proposed mechanism of nanoparticle induced degradation of PEGDTT. Adsorbed sodium cation gradually releases from nanosilicates surface resulting in the solution achieving a pH of 9.4 which accelerates PEGDTT degradation. (d) Swelling characteristics of 3D printed structure of PEGDTT (10% wt/vol)/nSi (4% wt/vol) bioink after 1 hr in PBS (n=9, *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc testing).