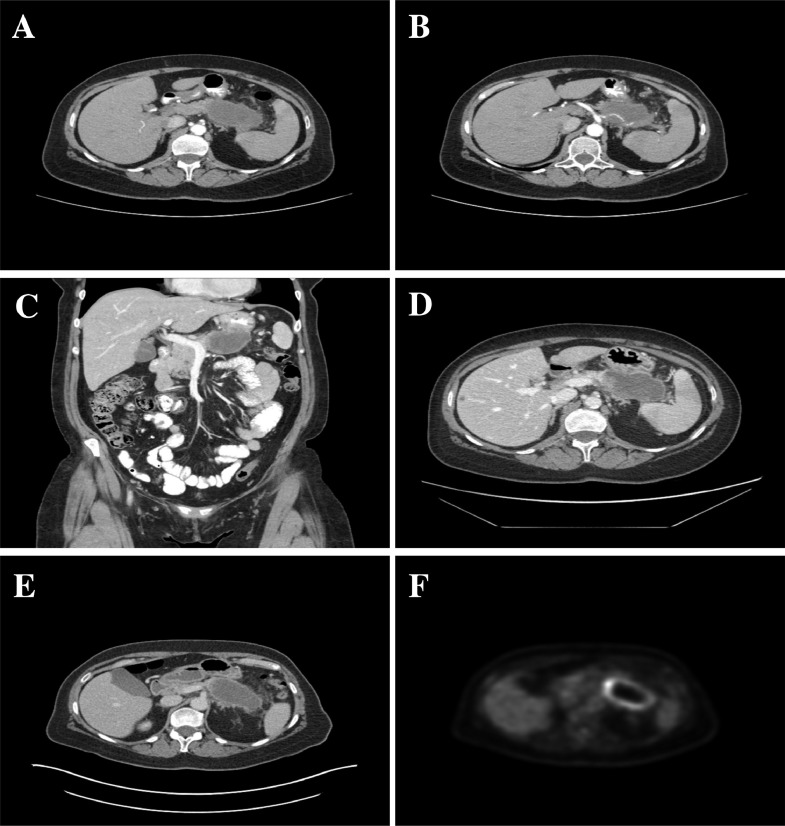
Fig. 1.
Case 1: Contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen showing a lobulated mass with peripheral ring enhancement and central hypoattenuation (A) invading the posterior gastric wall (B and C). Encasement of the splenic artery (B) and occlusion of the splenic vein (E) resulting in multiple splenic infarcts (A, B, and D). Solitary hypoattenuating metastasis in segment 5 of the liver (D). FDG-PET shows a peripheral ring of hypermetabolism and central hypometabolism corresponding to an area of necrosis (SUVMAX = 15 g/mL; F).