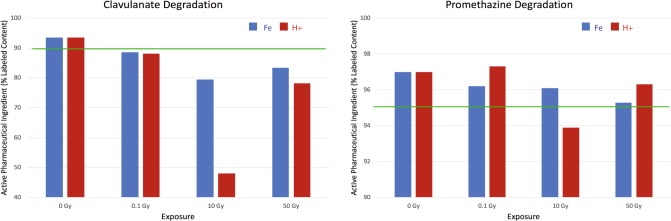
Fig. 2.
NASA data from an NSRL study performed by Daniel et al. demonstrating variable drug sensitivity to radiation exposure for clavulanate (as a combination medication, amoxicillin-clavulanate) and promethazine.20 All drug products were measured at time zero; control and irradiated products were analyzed at the same time following exposures. The solid green line indicates USP-accepted lower limits of percent API content compared to label claims. Note the variable sensitivity both by radiation beam exposure (proton, in red, or iron, in blue) and by dose received (0.1–50 Gy). In this study, drugs demonstrated increased degradation to 10 Gy exposures compared to 50 Gy exposures, suggesting that pharmaceutical stability at higher dose exposure may not necessarily translate to stability at lower dose exposures. However, the dose and dose-rate of high exposures were significantly greater than even cumulative anticipated doses in long-duration, exploration spaceflight. Further, there is only limited documentation regarding research design or even the full results of this study, limiting our ability to interpret the findings