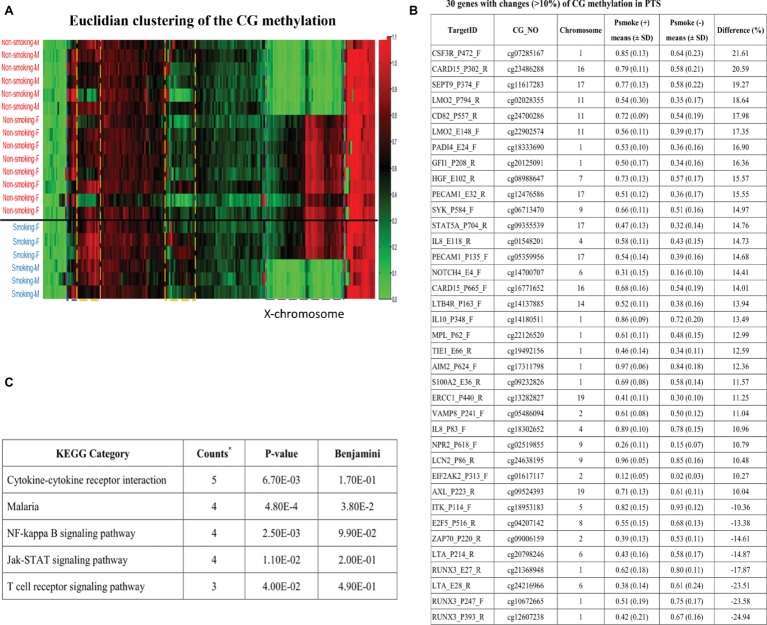
Figure 1.
Euclidian clustering of the CG methylation profiles between newborns with and without PTS. (A) Female (F) X-chromosome revealed one half of the CG sites were methylated (red color) but not male (M) ones (green), and there are other gene clusters associated with prenatal exposure of PTS (data deposited to the GEO Repository at accession number GSE129751); (B) Thirty-seven CG sites in 30 genes had 10% higher or lower CG methylated contents, in which 29 CG sites were higher and 8 CG sites were lower CG methylation; (C) The KEGG pathway analysis found five pathways including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, malaria defense, NF-kappa B signaling, Jak-STAT signaling, and T cell receptor signaling pathways were significantly involved in CG methylation changes associated with prenatal exposure of PTS. The five genes in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction are IL8, MPL, CSF3R, IL10, and LTA; the four genes in Malaria defense are IL8, HGF, IL10, and PECAM1; the four genes in NF-kappa B signaling pathway are IL8, LTA, SYK, and ZAP70; the four genes in Jak-STAT signaling pathway are MPL, CSF3R, IL10 and STAT5A; and the three genes in T cell receptor signaling pathway are ITK, IL10, and ZAP70.