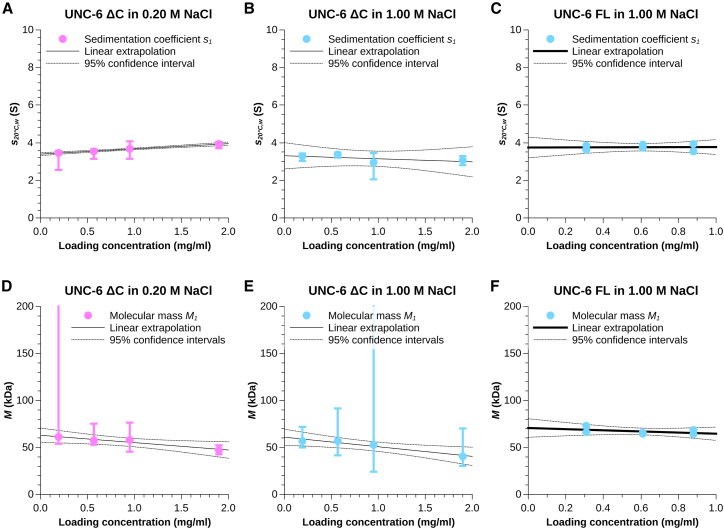
Figure 4.
(A and D) Sedimentation coefficients (A) and molecular masses (D) of monomeric UNC-6 ΔC (species 1) in low-ionic strength buffer as determined by separately fitting a hybrid model of a continuous c(s) distribution and two discrete species to the SV data measured at each protein loading concentration. (B and E) Sedimentation coefficients (B) and molecular masses (E) of monomeric UNC-6 ΔC (species 1) in high-ionic strength buffer as determined by separately fitting a noninteracting discrete species model with two discrete species to the SV data measured at each protein loading concentration. (C and F) Sedimentation coefficients (C) and molecular masses (F) of monomeric UNC-6 FL (species 1) in high-ionic strength buffer as determined by separately fitting a noninteracting discrete species model with three discrete species to the SV data measured at each protein loading concentration. Vertical error bars indicate the 95.4% confidence interval of the respective parameter at each loading concentration. The parameters were extrapolated (without weighting) to infinite dilution (black line) to account for protein-buffer interactions. The 95.4% confidence intervals of the extrapolation are shown by black dotted lines. To see this figure in color, go online.