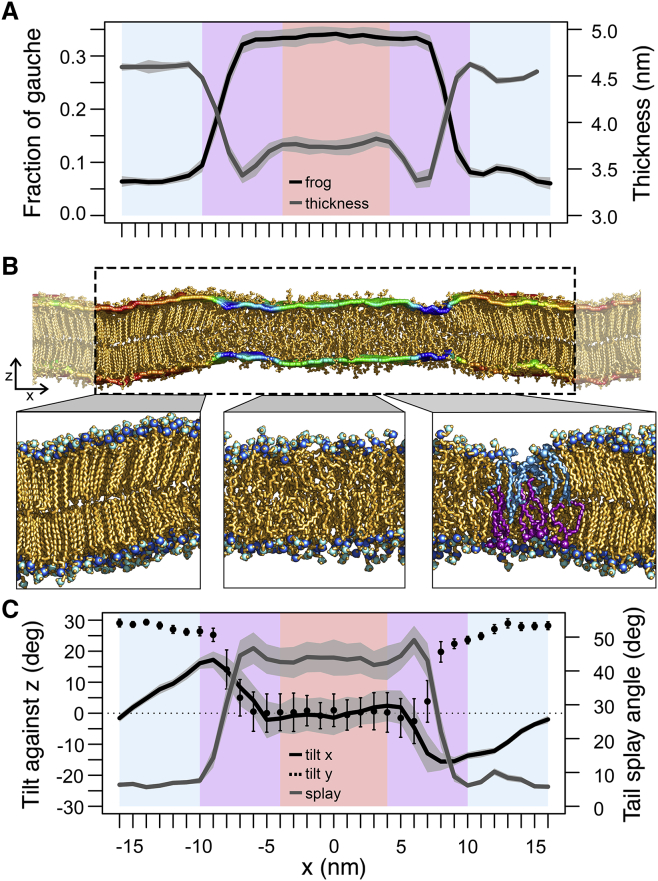
Figure 1.
Structural characteristics of a DPPC bilayer with coexisting fluid and gel phase domains (DPPCgf system). (A) Fraction of gauche (black line) and thickness (gray line) profiles across the interface (along the x axis) are shown. The blue, purple, and red backgrounds correspond to the gel, interface, and fluid domains, respectively. (B) A snapshot of the two-phase bilayer at the end of the simulation (100 ns) is shown. The bilayer thickness is superimposed on the headgroup region as a rainbow-colored surface, the colors ranging from blue (thickness of 3 nm) to red (5 nm). (C) Profiles of lipid tilt angle against z axis (black lines) are shown. The tilt in the x-direction (i.e., projection of the lipid tails on the xz-plane; see Fig. S1C) is given as a solid line, the tilt in the y-direction (i.e., projection of the lipid tails on the yz-plane) as dotted line (see also Fig. S1B). The gray line represents the lipid tail splay angle profile. All profile values were averaged over the final 50 ns. The SD is given as shaded area for all profiles except for the tilt in the y-direction, where it is represented as error bars. To see this figure in color, go online.