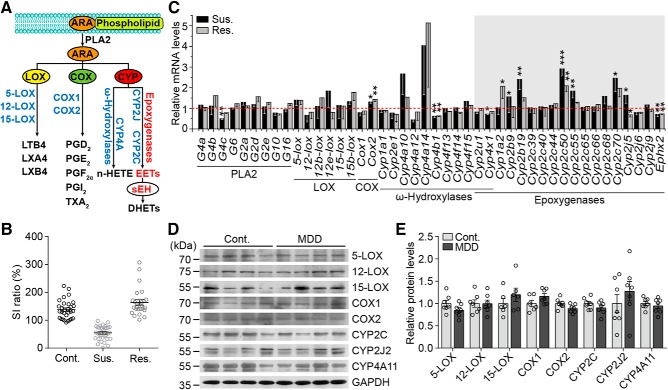
Figure 1.
ARA metabolic pathways in the mouse model and patients with MDD. A, Schematic representation of the ARA metabolic pathway. PLA2 enzymes are crucial for transferring esterified ARA to free ARA for metabolism. Three members of the PLA2 superfamily have been implicated most strongly in eicosanoid production, including cytosolic calcium-dependent PLAs [group (G) 4a–c], cytosolic calcium-independent PLA2 (G6), and secreted PLA2 (G2a, b, e and G10). Adipose-specific PLA2 is G16. The free ARA can be converted to eicosanoids via three pathways: the LOX, COX, and CYP. B, Identification of susceptible and resilient mice following the CSDS paradigm. Mice were divided into different groups by the SI ratio. Cont., Control; Sus., susceptible; Res., resilient. C, mRNA levels (relative to the control, red dashed line) of gene profiles related to the ARA KEGG pathway in the mPFC of adult C57BL/6J mice after CSDS. For qPCR primers, see Figure 1-1. D, E, Western blots and quantification of LOXs, COXs, and CYPs in the BA24 of subjects with MDD and matched controls. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.