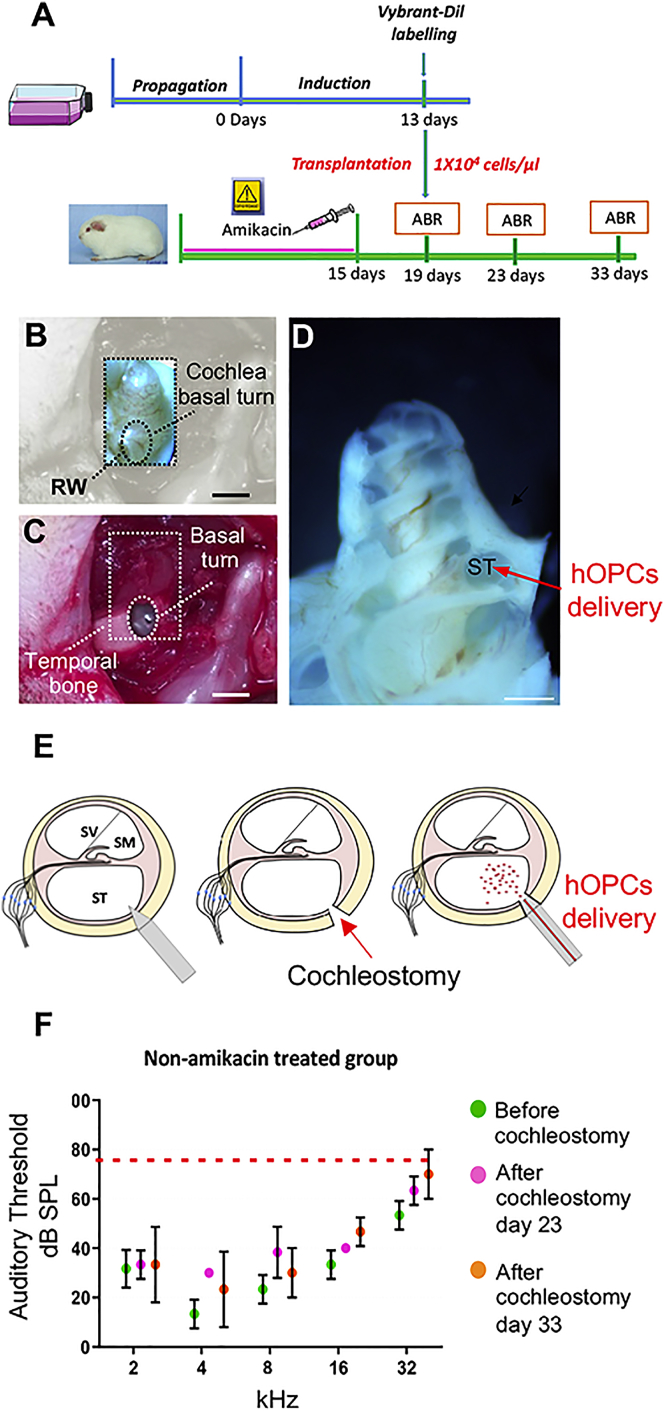
Figure 2.
Surgical Approach for Cell Injection into the Scala Tympani
(A) Timeline of human iPSC-derived otic progenitors in vitro and in vivo transplantation in adult guinea pig model of ototoxicity. (B–D) The anatomical landmarks used to ensure that the site of cochleostomy was consistent between animals are shown. A cochleostomy was performed at the base of the cochlea; dashed box in (B) and (C) and red arrow in (D) driving the cells into the scala tympani. (E) Schematic representation of sequential steps to inject hOPCs into the scala tympani by cochleostomy. (F) ABR measurements were performed on amikacin-untreated animals before cochleostomy (D19), 4 days after cochleostomy (D23), and 14 days after cochleostomy (D33). Auditory threshold values of pooled data (n ≥ 3 per group) are represented by the means (dot) ± SD (error bar). Wilcoxon rank-sum test, no statistically significant differences were found between groups before and after cochleostomy. RW, round window; ST, scala tympani. Scale bars, 500 μm.