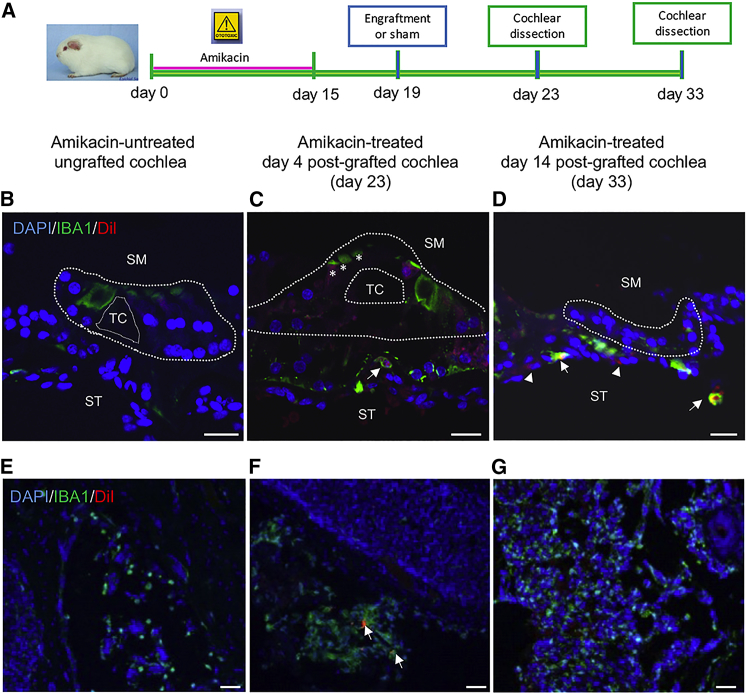
Figure 4.
Human Otic Progenitors Trigger an Immune Reaction after Transplantation
(A) Timeline of experimental design for hOPC transplantation into control and implanted drug-exposed cochleae. (B–D) IBA1-immunopositive cells (shown in green) are revealed by immunohistochemistry on transverse sections from cochleae of control untreated (B), no-implanted, 4 days post-implanted (C), and 14 days post-implanted drug-treated animals (D). The Vybrant-Dil-labeled cells are shown in red. Some of IBA1-immunopositive cells are observed at the basal part of the damaged organs of Corti (arrows). A slight IBA1 immunoreactivity was detected in some hair cells mostly those of amikacin-treated day 4 post-grafted cochlea (C, asterisks). Arrowheads show Dil-positive/IBA1 negative cells in (D). (E–G) Representative images from the modiolus areas of amikacin-untreated ungrafted animals (E) and amikacin-treated day 33 post-grafted animals (G) showing expression of IBA1 in many cells. (F) In the modiolus of amikacin-treated day 4 post-grafted animals, few Dil-labeled cells (shown in red, arrows) were surrounded by IBA1 immunostaining (shown in green, arrows). Nuclei were revealed by DAPI staining (shown in blue). Scale bars, 20 μm in all panels. SM, scala media; ST, scala tympani; TC, tunnel of Corti.