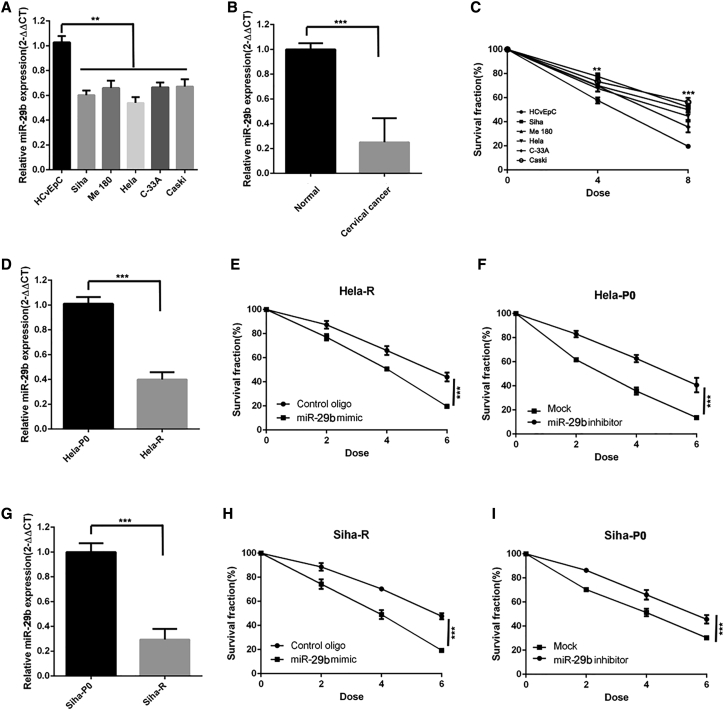
Figure 1.
miR-29b Increases Radiosensitivity and Is Downregulated in Radioresistant Cervical Cancer Cells
(A) qPCR of miR-29b of normal cervical cell line (HCvEpc) and cervical cancer cell lines (Siha, Me 180, HeLa, C-33A, Caski). n = 3 samples per group. (B) qPCR of miR-29b of normal cervical tissue and cervical cancer tissues. n = 8 samples per group. (C) Clonogenic survival assays of normal cervical cell line and cervical cancer cell lines. n = 3 samples per group. (D) qPCR of miR-29b of HeLa-R cells relative to HeLa-P0 cells. n = 3 samples per group. (E) Clonogenic survival assays of HeLa-R cells transduced with miR-29. n = 3 wells per group. (F) Clonogenic survival assays of HeLa-P0 cells transfected with the miR-29 inhibitor. n = 3 wells per group. (G) qPCR of miR-29b of Siha-R cells relative to Siha-P0 cells. n = 3 samples per group. (H) Clonogenic survival assays of Siha-R cells transduced with miR-29. n = 3 wells per group. (I) Clonogenic survival assays of Siha-P0 cells transfected with the miR-29 inhibitor. n = 3 wells per group. Data are the mean of biological replicates from a representative experiment, and error bars indicate SEM. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. The experiments were repeated three times. **p < 0.035; ***p < 0.01.