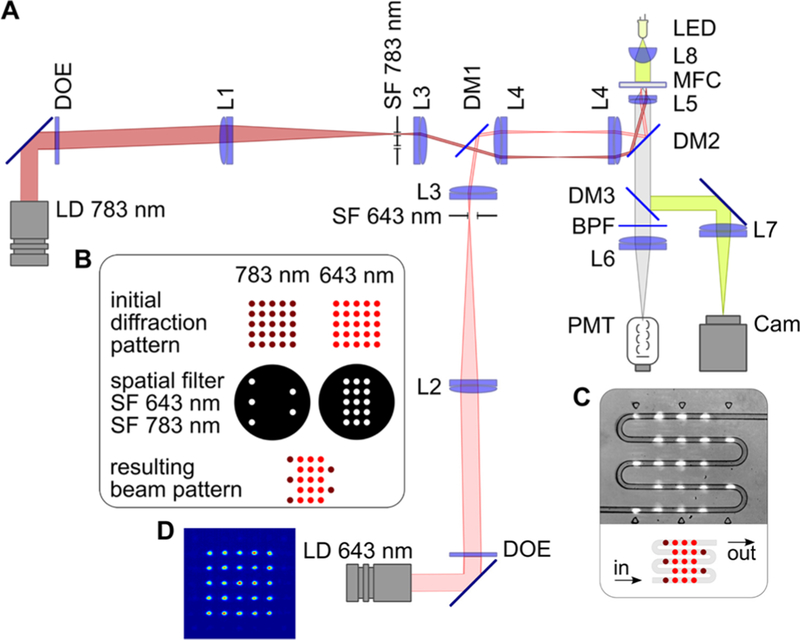
Figure 2.
Experimental setup. (A) Optical scheme, where laser diode (LD) modules emitting at 643 and 783 nm, diffractive optical elements (DOEs), lenses L1–L5, dichroic mirrors DM1 and DM2, and custom-made spatial filters (SF 643 nm and SF 783 nm) comprise the illumination arms of the system. The detection part consists of a dichroic mirror (DM3), a bandpass filter (BPF), a lens (L6), and a photomultiplier tube (PMT). Lenses L5 and L7, and the light-emitting diode (LED), comprise the trans-illumination bright-field microscope used for targeting and monitoring. (B) Formation of the multiple-beam structured illumination pattern. (C) Schematic and microscopic image of interrogation region of the microfluidic chip with serpentine channel, where droplets interact with laser beams. (D) Intensity distribution in the initial 643 nm diffraction pattern.