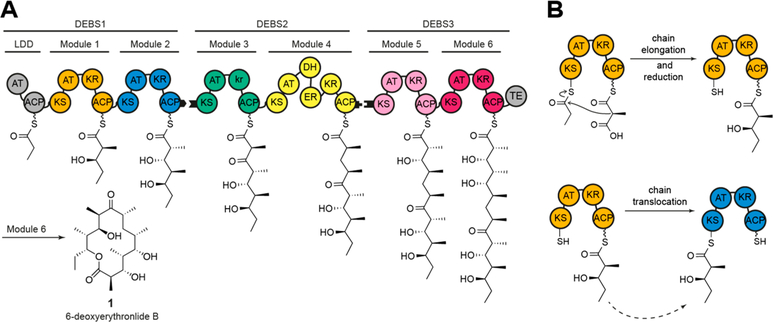
Figure 1.
Schematic architecture of DEBS. (A) The three polypeptides (DEBS1–3) and the encoded modules (M1–M6), as well as the loading didomain (LDD), the thioesterase domain (TE), and the final product (1) are depicted. Polyketide intermediates are shown as attached to the respective acyl carrier protein (ACP). Black tabs depict docking domains. Domain annotations are as follows: AT, acyltransferase; KS, ketosynthase; ACP, acyl carrier protein; KR, ketoreductase; DH, dehydratase; ER, enoylreductase. Module 3 has a ketoreductase-like domain (denoted in lowercase) that lacks NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase activity but harbors C-2 epimerase activity. (B) The intramodular chain elongation and intermodular chain translocation steps are shown for M1. The ACP of this module carries the α-carboxyacyl-chain (methylmalonyl-ACP) or the (2S,3R)-2-methyl-3-hydroxy-diketide condensation product.